Abstract
Concentration quenching is a well-known challenge in many fluorescence imaging applications. Here, we show that the optical emission from hundreds of chromophores confined onto the surface of a 28 nm diameter virus particle can be recovered under pulsed irradiation. We have found that as one increases the number of chromophores tightly bound to the virus surface, fluorescence quenching ensues at first, but when the number of chromophores per particle is nearing the maximum number of surface sites allowable, a sudden brightening of the emitted light and a shortening of the excited-state lifetime are observed. This radiation brightening occurs only under short pulse excitation; steady-state excitation is characterized by conventional concentration quenching for any number of chromophores per particle. The observed suppression of fluorescence quenching is consistent with efficient, collective relaxation at room temperature. Interestingly, radiation brightening disappears when the emitters’ spatial and/or dynamic heterogeneity is increased, suggesting that the template structural properties may play a role that could be instrumental in developing virus-enabled imaging vectors that have optical properties qualitatively different than those of state-of-the-art biophotonic agents. - Copyright © 2019 American Chemical Society
Latest Publications
Dragnea Research is at the forefront of multidisciplinary innovation, exploring the intersection of nanoscale optics, quantum photonics, physical virology, and bio-architected hybrid materials with 3D nanoscale order. Their latest publications highlight groundbreaking advancements in fields such as self-assembly, optics and spectroscopy, and the physical manipulation of virus-like particles (VLPs) for chemical imaging and surface modifications. Drawing from their expertise in using near-field scanning techniques and laser-induced effects, these works showcase how nanoscale phenomena can be harnessed for applications in material science, virology, and beyond. The accompanying visual mosaic underscores the diverse range of their research, from probing molecular dynamics to the development of 3D-ordered structures, all united by a commitment to pushing the boundaries of applied and theoretical science.
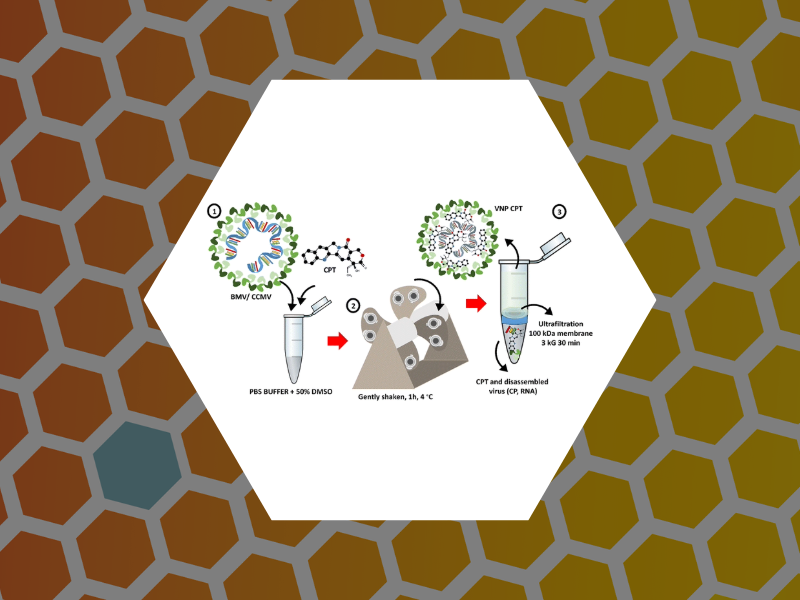
117. The solvent stability of bromovirus allows for delivery of hydrophobic chemotherapeutic drugs. E. Loredo-García, M.M. Herrera-Hernandez, C. Medrano-Villagómez, P. Fournier, A.G. Rodríguez-Hernández, M. Loredo-Tovías, J. Ruiz-Garcia, B. Dragnea, & R.D. Cadena-Nava, Materials Advances (2025)
116. Nanotribology of viruses reveals their adhesion strength and modality of motion on surfaces. C. Ault, C. Simon, I.B. Tsvetkova, P.J. De Pablo, B. Dragnea Frontiers in Biophysics (2025)
115. Genetically Engineered, Multichromophore Virus-Like Nanoparticles with Ultranarrow Distribution of Emission Intensity. Irina B Tsvetkova, Nora Roos, Lohra M Miller, Nadia DiNunno, Marcel Conrady, Domenic Ebert, Hauke Lilie, Liam W Scott, Martin F Jarrold, Joseph Che-Yen Wang, Claudia Simon, Bogdan Dragnea ACS Nano (2025), 19 (1), 479-487
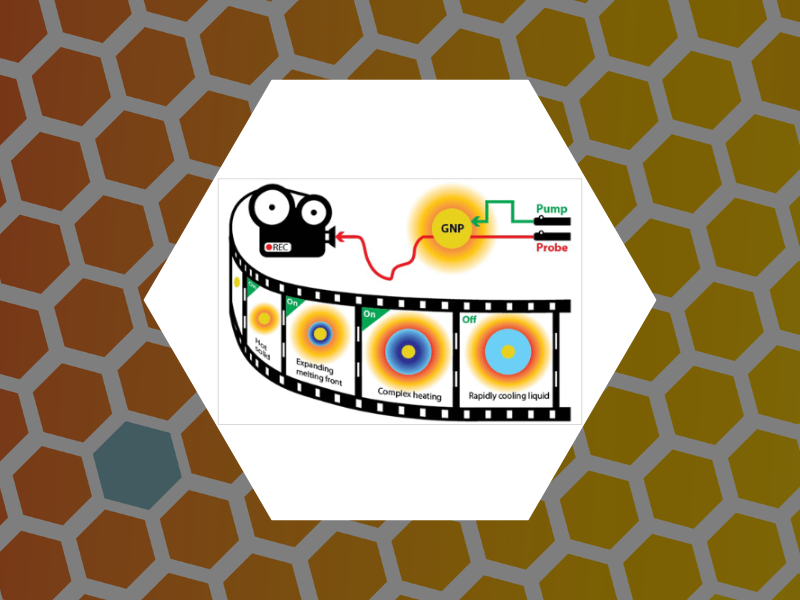
114. Real-Time Optical Measurements of Nanoparticle-Induced Melting and Resolidification Dynamics. Jo, Suhun; Schaich, William L. and Dragnea, Bogdan ACS Nano (2023), 17(1), 505-514 DOI:10.1021/acsnano.2c09212

113. A three-dimensional discrete model for approximating the deformation of a viral capsid subjected to lying over a flat surface in the static and time-dependent case. Piersanti, Paolo; White, Kristen; Dragnea, Bogdan and Temam, Roger Analysis and Applications (2022), 20(6), 1159-1191, DOI: 10.1142/S0219530522400024
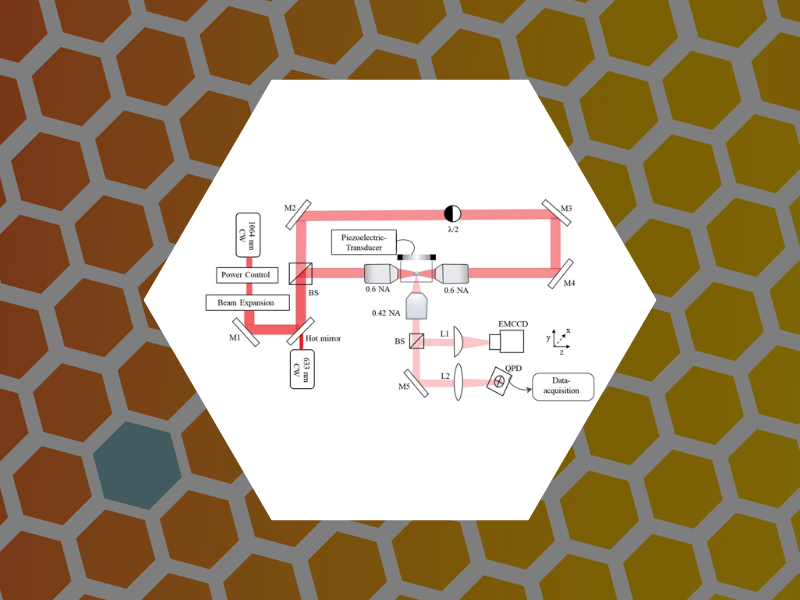
112. Orbital Dynamics at Atmospheric Pressure in a Lensed, Dual-beam, Optical Trap. Raj, Amala; Schaich, William L. and Dragnea, Bogdan Journal of the Optical Society of America A (2022), 39(8),1468-1478 DOI:10.1364/JOSAA.459301

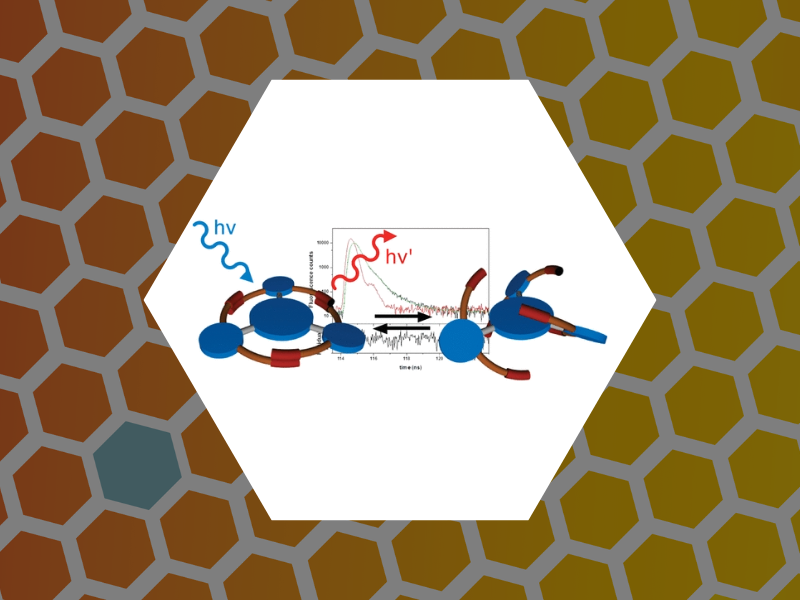
111. Ultrafast Collective Excited-State Dynamics of a Virus-Supported Fluorophore Antenna. Holmes, Joseph; Anil Sushma, Arathi; Tsvetkova, Irina B.; Schaich, William L.; Schaller, Richard D. and Dragnea, Bogdan Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (2022), 13(14), 3237-3243, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.2c00262

110. Modelling Virus Contact Mechanics Under Atomic Force Imaging Conditions. Piersanti, Paolo; White, Kristen; Dragnea, Bogdan and Temam, Roger Applicable Analysis (2022), DOI: 10.1080/00036811.2022.2044027
109. Virus Assembly Pathways Inside a Host Cell. Panahandeh, Sanaz; Li, Siyu; Dragnea, Bogdan and Zandi, Roya ACS Nano (2022), 16(1), 317-327 DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.1c06335
108. Hydrophobic Cargo Encapsulation into Virus Protein Cages by Self-Assembly in an Aprotic Organic Solvent. Xie, Amberly; Tsvetkova, Irina B.; Liu, Yang; Ye, Xingchen; Hewavitharanage, Priyadarshine; Dragnea, Bogdan and Cadena-Nava, Ruben D. Bioconjugate Chemistry (2021), 32(11), 2366-2376, DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.1c00420
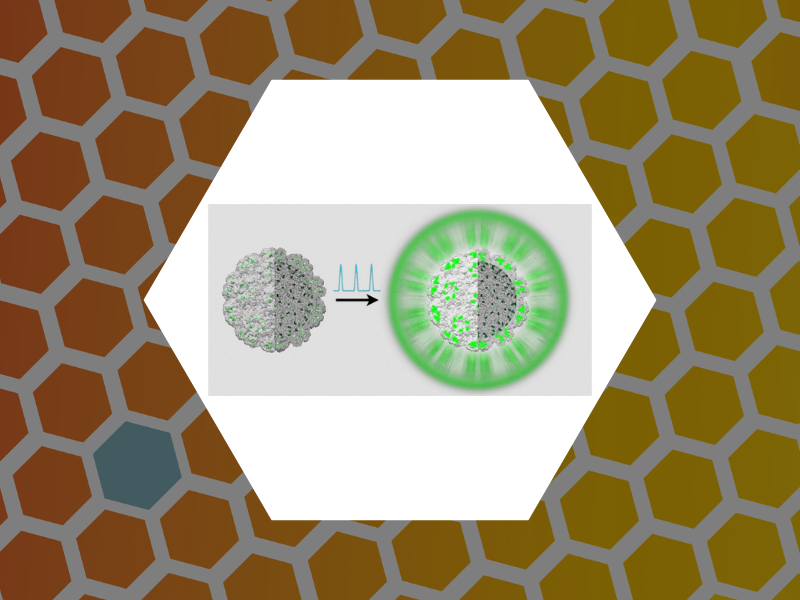
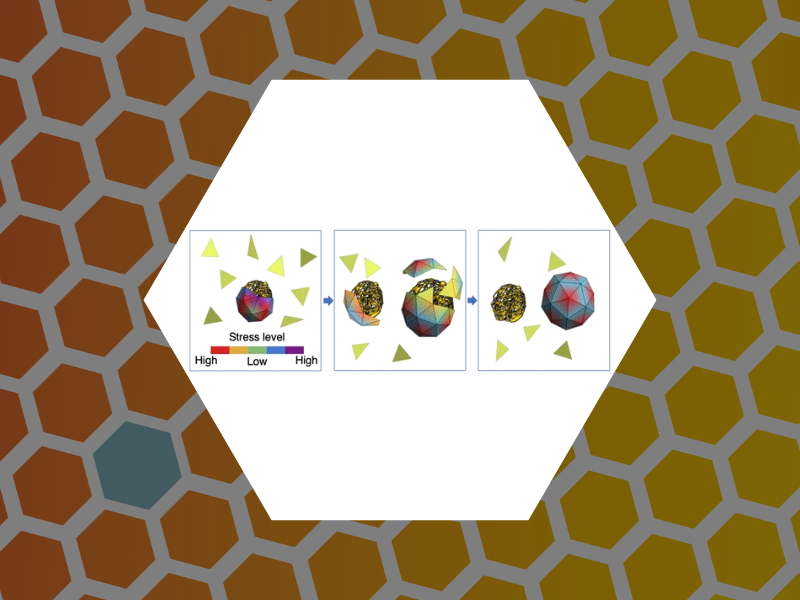
107. Subset of Fluorophores Is Responsible for Radiation Brightening in Viromimetic Particles. Anil Sushma, Arathi; Zhao, Bingqing; Tsvetkova, Irina B.; Perez-Segura, Carolina; Hadden-Perilla, Jodi A.; Reily, James P. and Dragnea, Bogdan Journal of Physical Chemistry B (2021), 125(37), 10494-10505, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.1c06395
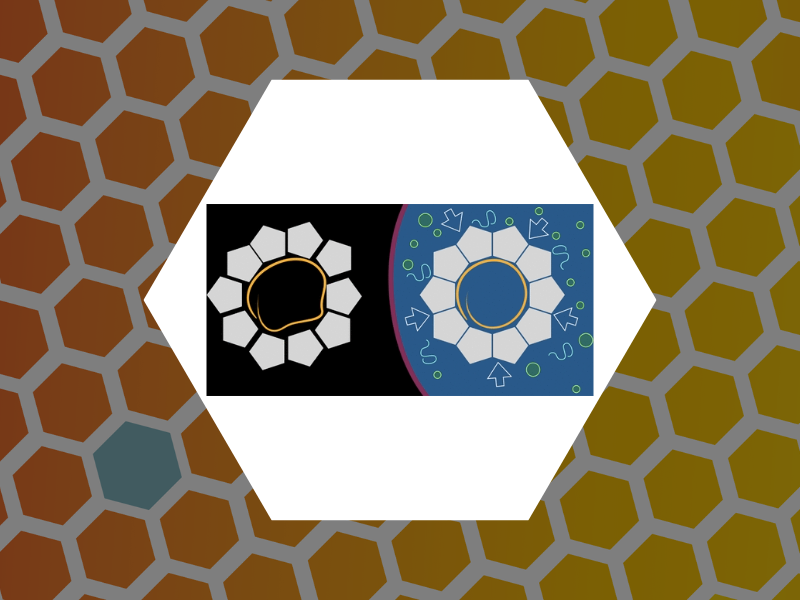
106. Virus Mechanics under Molecular Crowding. Zang, Cheng; Scott, Liam; Malyutin, Andrey; Zandi, Roya; van der Schoot, Paul and Dragnea, Bogdan Journal of Physical Chemistry B (2021), 125(7), 1790-1798, DOI:10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c10947

105. Virus Assembly Pathways: Straying Away but Not Too Far. Bond, Kevin; Tsvetkova, Irina; Wang, Joseph C.-Y.; Jarrold, Martin F. and Dragnea, Bogdan Small (2020), 16, 2004475, doi:10.1002/smll.202004475
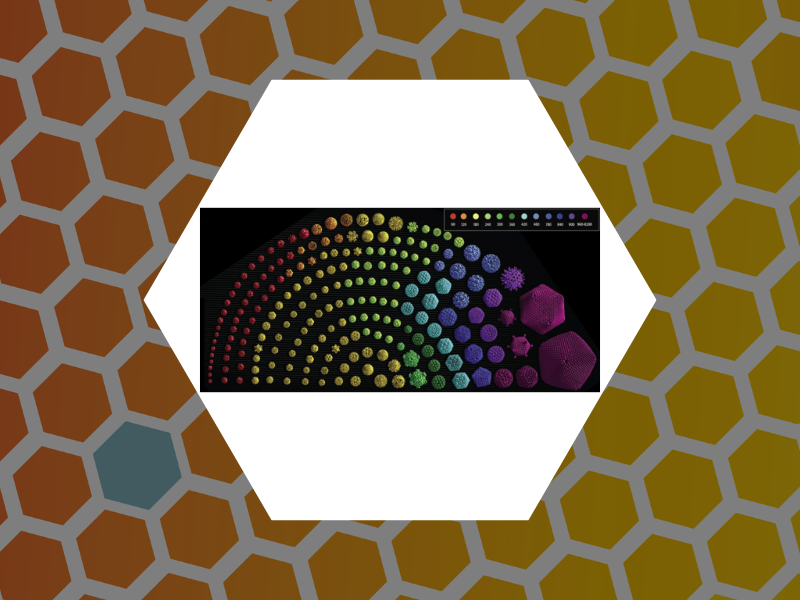
104. A Laboratory Model for Virus Particle Nanoindentation. Thompson, William C.; Cattani, Angela J.; Lee, Olive; Ma, Xiang; Tsvetkova, Irina B. and Dragnea, Bogdan The Biophysicist (2020), 1(2), 5, DOI:10.35459/tbp.2019.000106
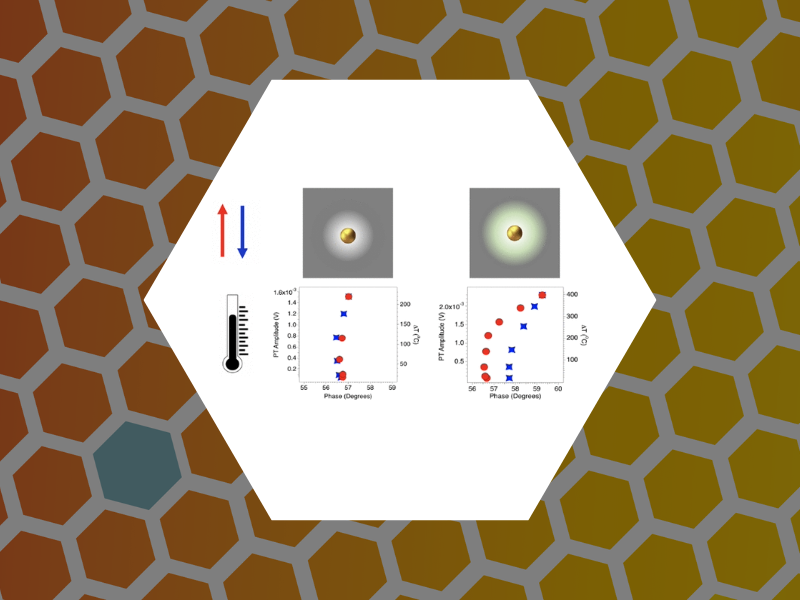
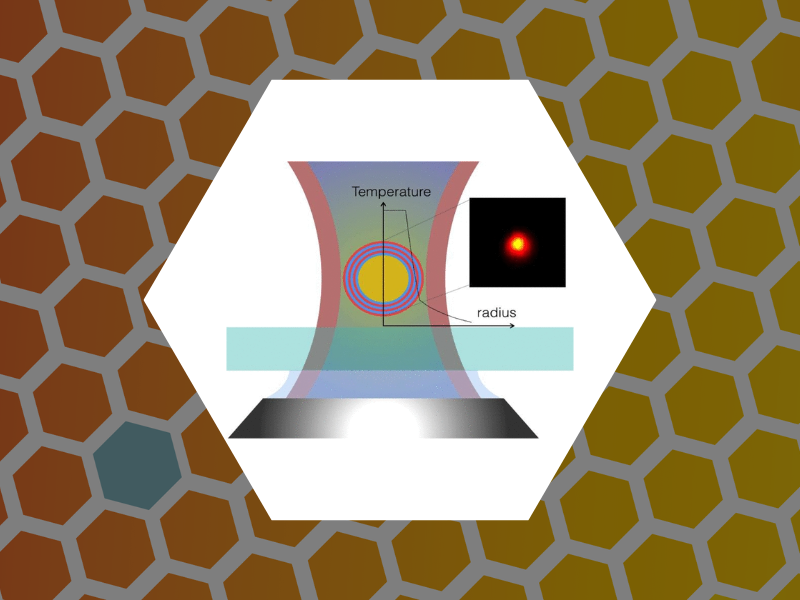
103. Studies of Nanoparticle-Assisted Photoannealing of Polydimethylsiloxane by Time-Harmonic Photothermal Microscopy. Zahedian, Maryam; Lee, Zachary; Koh, Eun Sohl and Dragnea, Bogdan ACS Photonics (2020), 7(9), 2601-2609, DOI:10.1021/acsphotonics.0c00968
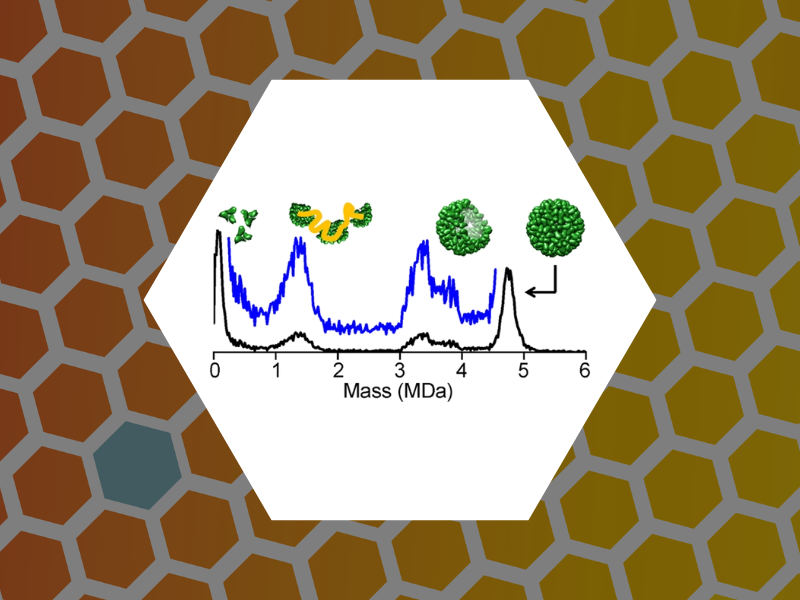
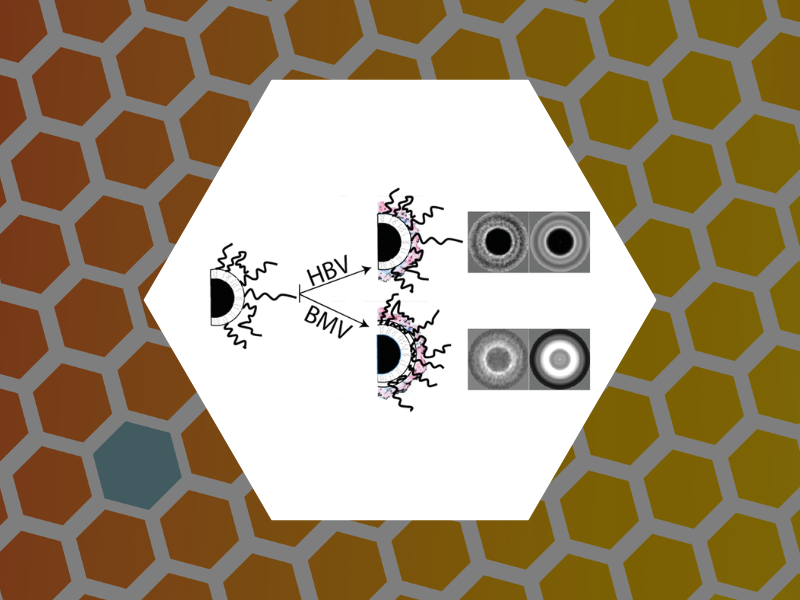
102.Disassembly Intermediates of the Brome Mosaic Virus Identified by Charge Detection Mass Spectrometry. Bond, Kevin; Lyktey, Nicholas; Tsvetkova, Irina; Dragnea, Bogdan and Jarrold, Martin Journal of Physical Chemistry B (2020), 124(11), 2124-2131, DOI:10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c00008

101. On virus growth and form. Zandi, Roya; Dragnea, Bogdan; Travesset, Alex and Podgornik, Rudolf Physics Reports (2020), 847, 1-102, DOI:10.1016/j.physrep.2019.12.005

100. Watching a virus grow. Dragnea, Bogdan Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2019), DOI:10.1073/pnas.1915986116
99. Photothermal microspectroscopy with Bessel-Gauss beams and reflective objectives. Zahedian, Maryam; Koh, Eun Sohl; Dragnea, Bogdan Applied Optics (2019), 58(27), 7352-7358, DOI:10.1364/AO.58.007352
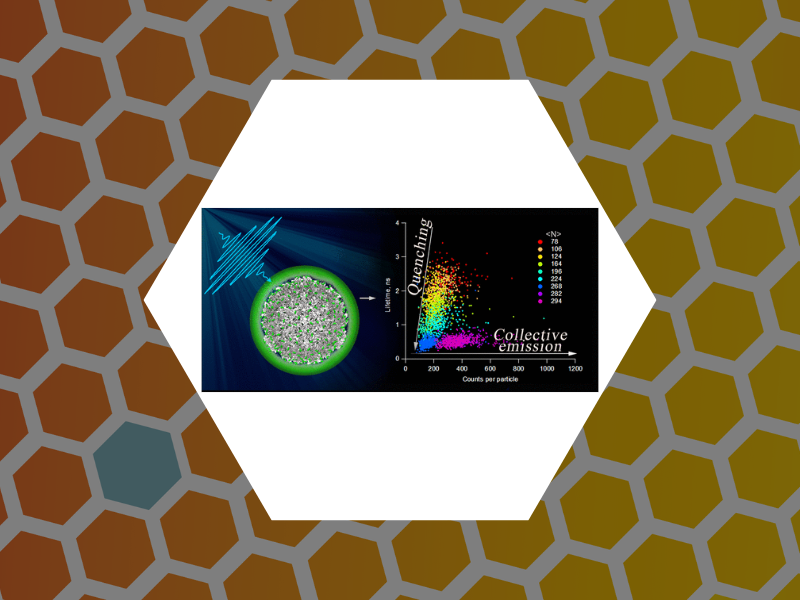
98. Radiation Brightening from Virus-like Particles. Tsvetkova, Irina B.; Anil Sushma, Arathi; Wang, Joseph C.-Y.; Schaich, William L.; Dragnea, Bogdan ACS Nano (2019), 13(10), 11401-11408, DOI:10.1021/acsnano.9b04786

97. Intermittency of Deformation and the Elastic Limit of an Icosahedral Virus under Compression. Hernando-Perez, Mercedes; Zeng, Cheng; Miguel, M. Carmen; Dragnea, Bogdan ACS Nano (2019), 13(7), 7842-7849, DOI:10.1021/acsnano.9b02133

96. In Vitro Assembly of Virus-Derived Designer Shells Around Inorganic Nanoparticles. Vieweger, Stella E.; Tsvetkova, Irina B.; Dragnea, Bogdan In: Wege C., Lomonossoff G. (eds) Virus-Derived Nanoparticles for Advanced Technologies. Methods in Molecular Biology (2018), vol 1776, Humana Press, New York, NY , DOI:10.1007/978-1-4939-7808-3_19
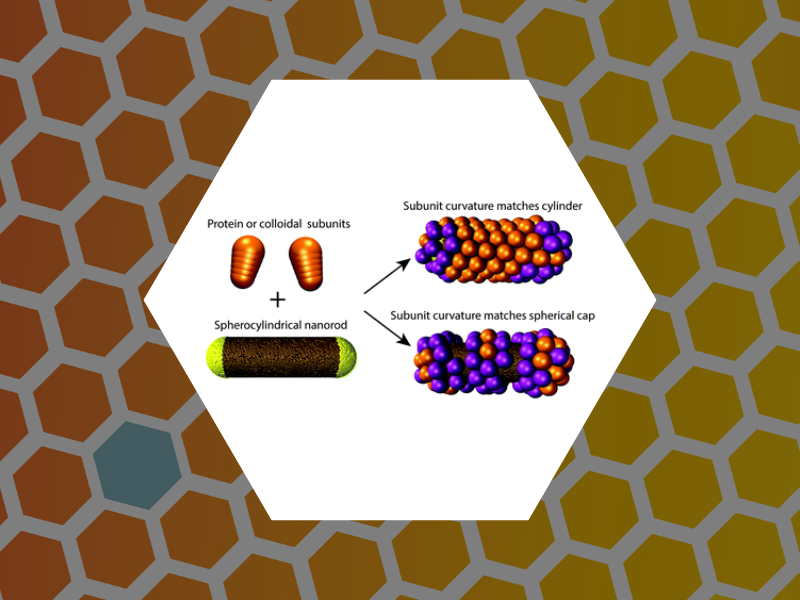
95. Self-assembly of convex particles on spherocylindrical surfaces. Lazaro, Guillermo Rodriguez; Dragnea, Bogdan; Hagan, Michael F. Soft Matter (2018), 14, 5728-5740, DOI:10.1039/C8SM00129D
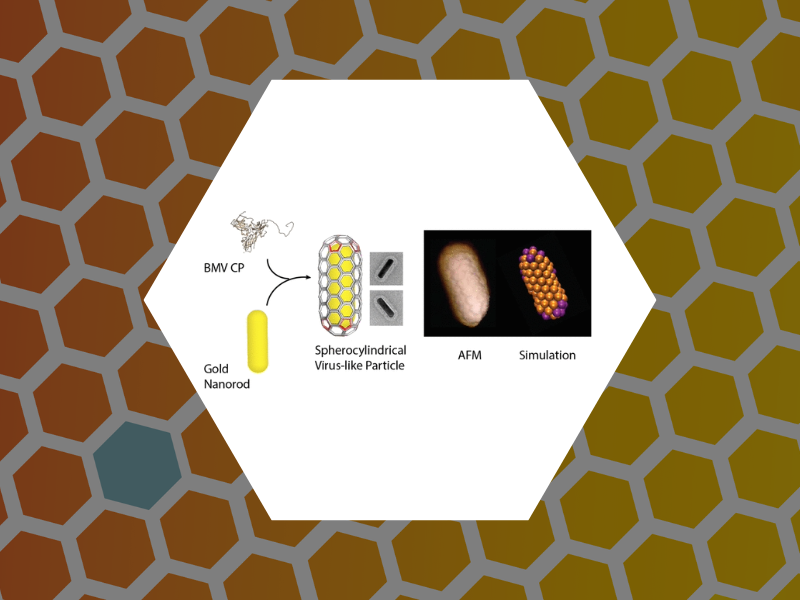
94. Defects and Chirality in the Nanoparticle-Directed Assembly of Spherocylindrical Shells of Virus Coat Proteins. Zeng, Cheng; Lazaro, Guillermo Rodriguez; Tsvetkova, Irina B.; Hagan, Michael F.; Dragnea, Bogdan ACS Nano (2018), 12(6), 5323-5332, DOI:10.1021/acsnano.8b00069
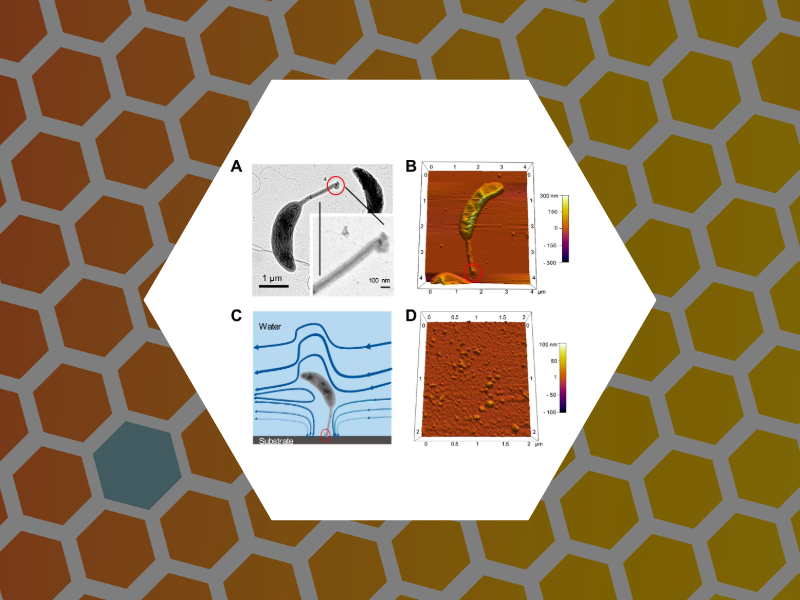
93. Layered Structure and Complex Mechanochemistry Underlie Strength and Versatility in a Bacterial Adhesive. Hernando-Perez, Mercedes; Setayeshgar, Sima; Hou, Yifeng; Temam. Roger; Brun, Yves; Dragnea, Bogdan; Berne, Cecile mBio (2018), 9(1). DOI:10.1128/mBio.02359-17

92. Contact Mechanics of a Small Icosahedral Virus. Zeng, Cheng; Hernando-Perez, Mercedes; Dragnea, Bogdan; Ma, Xiang; van der Schoot, Paul; Zandy, Roya Physical Review Letters (2017), 119(3), 038102. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.038102

91. Virus-Based Devices: Prospects for Allopoiesis. Dragnea, Bogdan ACS Nano (2017), 11(4), 3433-3437. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.7b01761
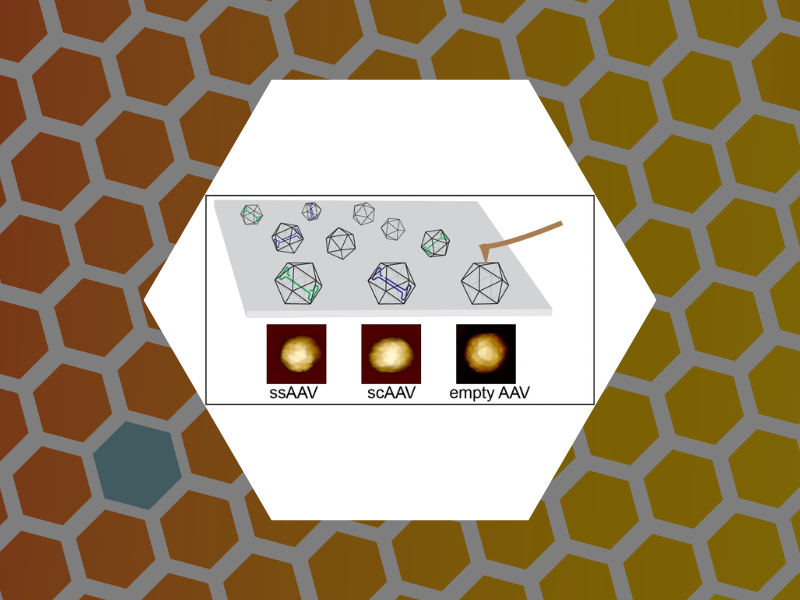
90. Probing the Link among Genomic Cargo, Contact Mechanics, and Nanoindentation in Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus 2. Zeng, Cheng; Moller-Tank, Sven; Asokan, Aravind; Dragnea, Bogdan Journal of Physical Chemistry B (2017), 121(8), 1843-1853. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b10131

89. Virus Matryoshka: A Bacteriophage Particle-Guided Molecular Assembly Approach to a Monodisperse Model of the Immature Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Saxena, Pooja; He, Li; Malyutin, Andrey; Datta, Siddhartha A. K.; Rein, Alan; Bond, Kevin M.; Jarrold, Martin F.; Spilotros, Alessandro; Svergun, Dmitri; Douglas, Trevor; Dragnea, Bogdan Small (2016), 12(42), 5862-5872. DOI: 10.1002/smll.201601712

88. Towards the modeling of nanoindentation of virus shells: Do substrate adhesion and geometry matter? Bousquet, Arthur; Dragnea, Bogdan; Tayachi, Manel; Temam, Roger Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena (2016), 336, 28-38. DOI:10.1016/j.physd.2016.06.013
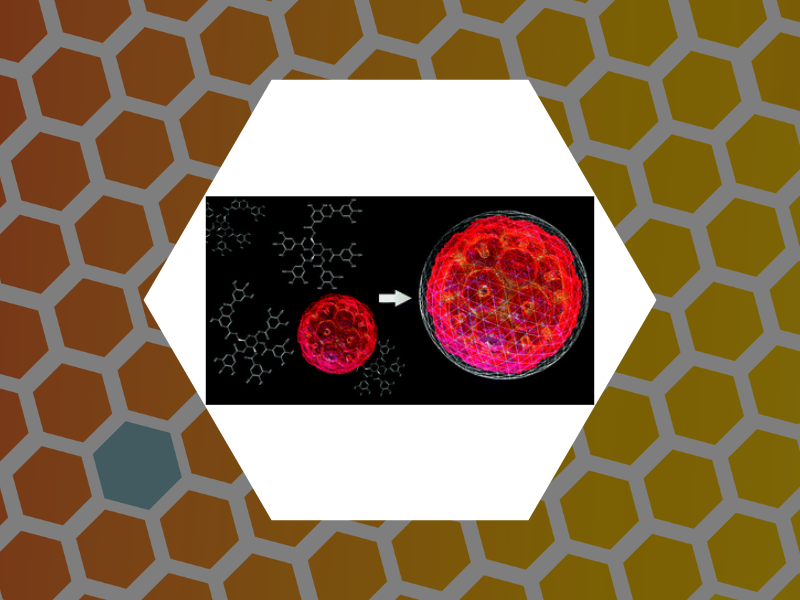
87. Catching a Virus in a Molecular Net. Delalande, Lily; Tsvetkova, Irina; Zeng, Cheng; Bond, Kevin; Jarrold, Martin F.; Dragnea, Bogdan Nanoscale (2016), 8, 16221-16228. DOI:10.1039/C6NR04469G. This article is part of themed collection: 2016 Nanoscale HOT Article Collection
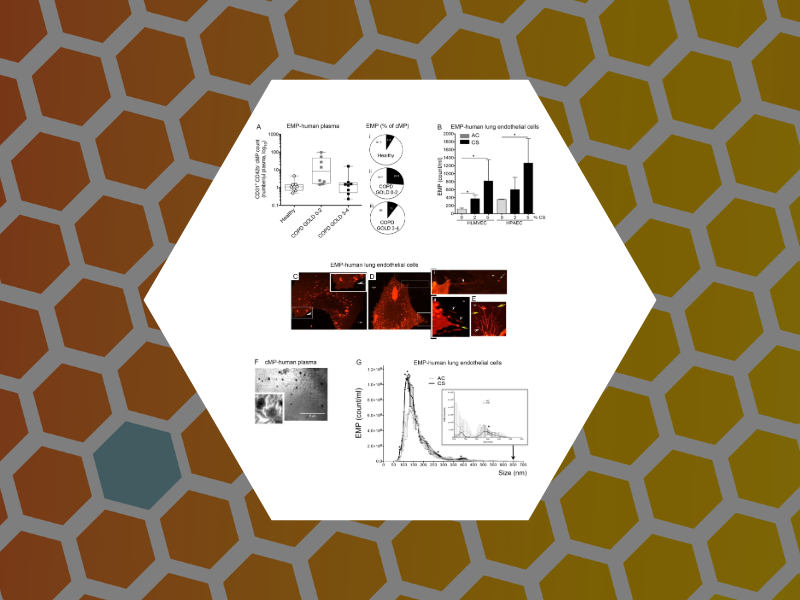
86. Structural and functional characterization of endothelial microparticles released by cigarette smoke. Serban, K.A.; Rezania, S.; Petrusca, D.N.; Poirier, C.; Cao, D.; Justice, M.J.; Patel, M.; Tsvetkova, I.; Kamocki, K.; Mikosz, A.; Schweitzer, K.S.; Jacobson, S.; Cardoso, A.; Carlesso, N.; Hubbard, W.C.; Kechris, K.; Dragnea, B.; Berdyshev, E.V.; McClintock, J.; and Petrache, I. Nature Scientific Reports (2016), 6, Article number: 31596, DOI:10.1038/srep31596
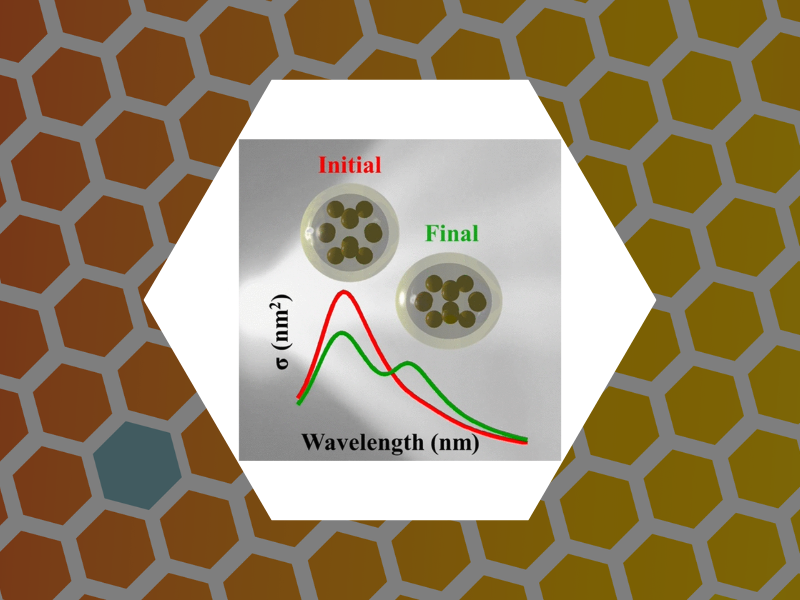
85. Towards Virus-Like Surface Plasmon Strain Sensors. Zahedian, Maryam; Huang, Xinlei; Tsvetkova, Irina B.; Rotello, Vincent M.; Schaich, William L.; Dragnea, Bogdan G. Journal of Physical Chemistry B (2016), 120(26), 5896-5906, DOI:10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b01023
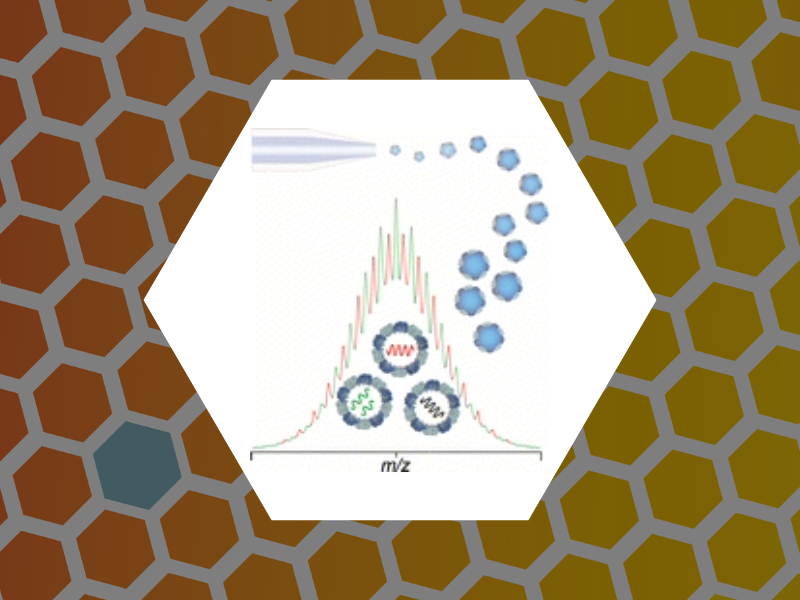
84. Examining the Heterogeneous Genome Content of Multipartite Viruses BMV and CCMV by Native Mass Spectrometry. van de Waterbeemd, Michiel; Snijder, Joost; Tsvetkova, Irina B.; Dragnea, Bogdan G.; Cornelissen, Jeroen J.; Heck, Albert J. R. Journal of The American Society for Mass Spectrometry (2016), 27(6), 1000-1009, DOI:10.1007/s13361-016-1348-6
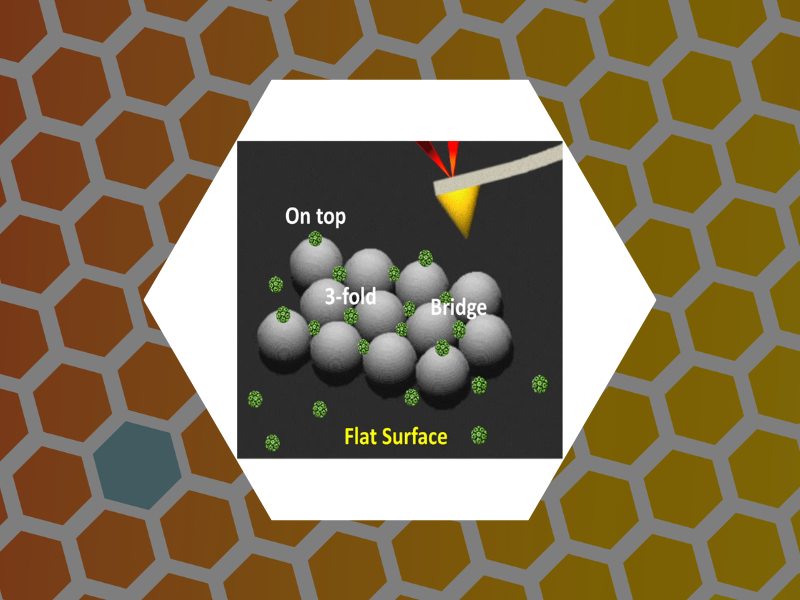
83. Nanoindentation of Isometric Viruses on Deterministically Corrugated Substrates. Hernando-Perez, Mercedes; Zeng, Cheng; Delalande, Lily; Tsvetkova, Irina B.; Bosquet, Arthur; Tayachi-Pigeonnat, Manel; Temam, Roger; Dragnea, Bogdan G. Journal of Physical Chemistry B (2016), 120(2), 340-347, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.5b08362
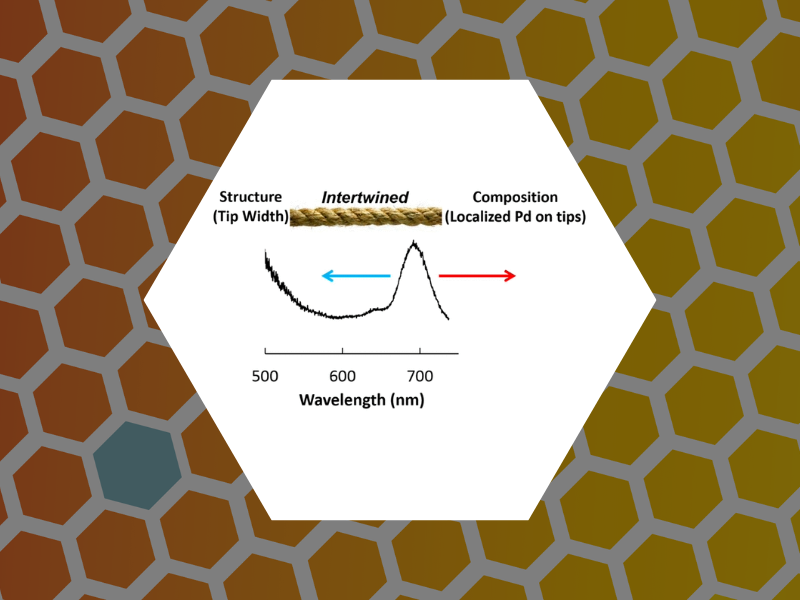
82. Structure versus Composition: A Single-Particle Investigation of Plasmonic Bimetallic Nanocrystals. Smith, Alison F.; Weiner, Rebecca G.; Bower, Matthew M.; Dragnea, Bogdan; Skrabalak, Sara E. Journal of Physical Chemistry C (2015), 119(38), 22114-22121.
81. Measurement of Nanoparticle Adlayer Properties by Photothermal Microscopy. Koh, Eun Sohl; McDonald, James; Tsvetkova, Irina B.; Dragnea, Bogdan G. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (2015), 6, 3621-3625.

80. Segmented GFP-like aptamer probes for functional imaging of viral genome trafficking. Tsvetkova, Irina B.; Yi, Guanghui; Yi, Yi; C. Cheng, Kao; Dragnea, Bogdan G. Virus Research (2015), 210, 291-297.

79. Principles of Design of Virus Nanoparticles for Imaging Applications. Tsvetkova, Irina B.; Dragnea, Bogdan G. Viral Nanothechnology, CRC Press (2015) 383-390.
78. Coat Protein-Dependent Behavior of Poly(ethylene glycol) Tails in Iron Oxide Core Virus-like Nanoparticles. Malyutin, Andrey G.;Cheng, Hu; Sanchez-Felix, Olivia R.; Carlson, Kenneth; Stein, Barry D.; Konarev, Petr V.; Svergun, Dmitri I.; Dragnea, Bogdan G.; Bronstein, Lyudmila M. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces (2015), 7 (22), 12089-12098.
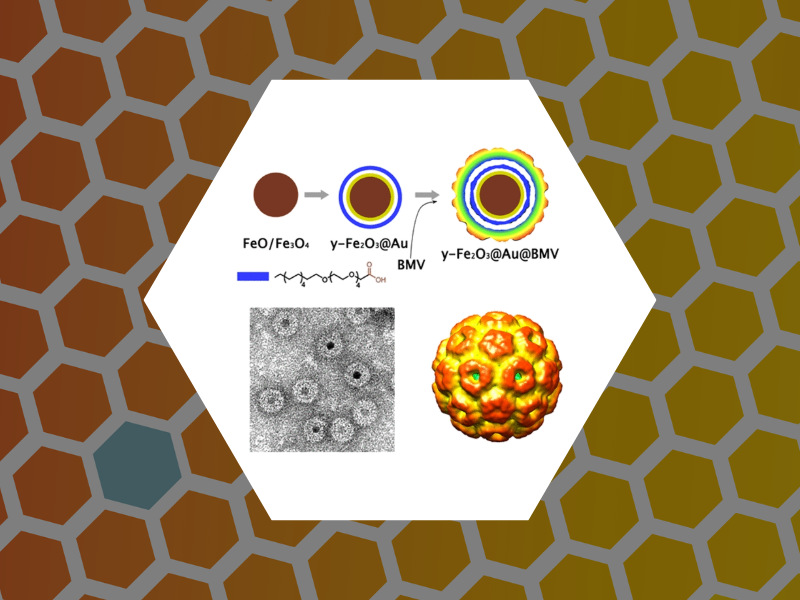
77. Viruslike Nanoparticles with Maghemite Cores Allow for Enhanced MRI Contrast Agents. Malyutin, Andrey G.; Easterday, Rosemary; Lozovyy, Yaroslav; Spilotros, Alessandro; Cheng, Hu; Sanchez-Felix, Olivia R.; Stein, Barry D.; Morgan, David Gene; Svergun, Dmitri I.; Dragnea, Bogdan; Bronstein, Lyudmila M.; Chemistry of Materials (2015), 27 (1), 327-335.

76. Role of Charge Regulation and Size Polydispersity in Nanoparticle Encapsulation by Viral Coat Proteins. Kusters, Remy; Lin, Hsiang-Ku; Zandi, Roya; Tsvetkova, Irina B; Dragnea, Bogdan; van der Schoot, Paul. Journal of Physical Chemistry B (2015), 119 (5), 1869-1880.

75. Encapsulation of nanoparticles in virus protein shells. Tsvetkova, Irina B; Dragnea, Bogdan. Protein Cages: Methods and Protocols (Methods in Molecular Biology) (2015) 1252:1-15.
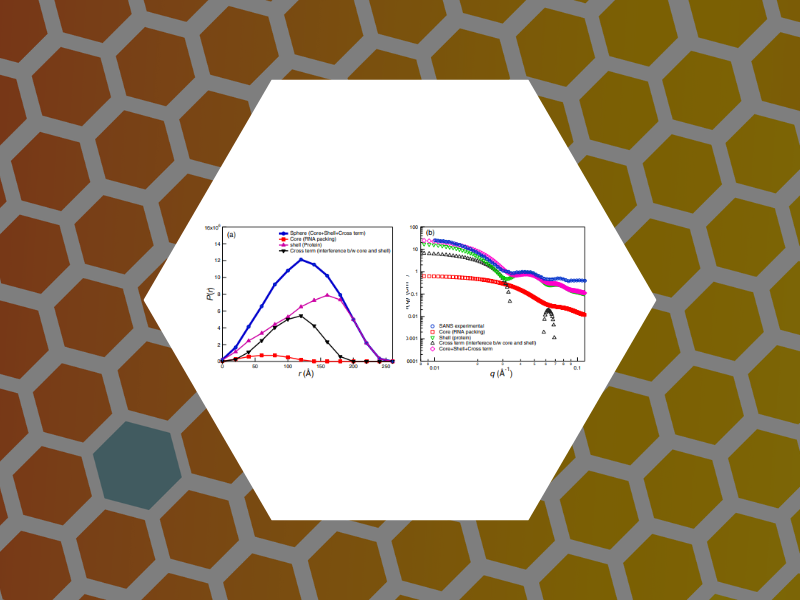
74. Small Angle Scattering Study of the Structure and Organization of RNAs and Protein of Brome Mosaic Virus (BMV) Capsid Protein. Das, Narayan Ch.; Warren, Garfield T.; Kao, Cheng C.; Dragnea, Bogdan G.; Ni, Peng; Sokol, Paul E. Physics Procedia (2014), 60, 101-109.

73. In Singulo Probing of Viral RNA Dynamics by Multi-chromophore Fluorescence Dequenching. Smith, Virginia; Dragnea, Bogdan. Journal of Physical Chemistry B (2014), 118 (49), 14345-14352.
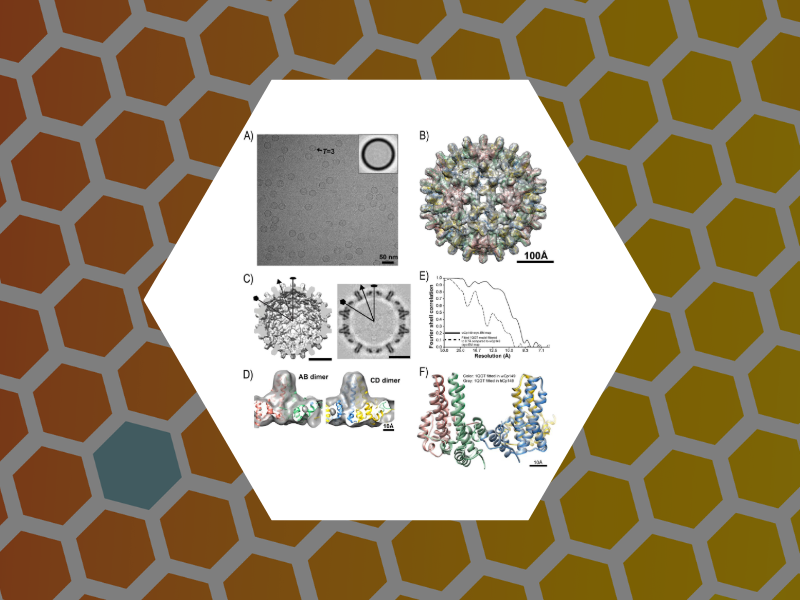
72. Structurally Similar Woodchuck and Human Hepadnavirus Core Proteins Have Distinctly Different Temperature Dependences of Assembly. Kukreja, Alexander A.; Wang, Joseph C.-Y.; Pierson, Elizabeth; Keifer, David Z.; Selzer, Lisa; Tan, Zhenning; Dragnea, Bogdan; Jarrold, Martin F.; Zlotnick, Adam. Journal of Virology (2014), 88 (24), 14105-14115.
71. The Tripartite Virions of the Brome Mosaic Virus Have Distinct Physical Properties that Affect the Timing of the Infection Process. Vaughan, Robert; Tragesser, Brady; Ni, Peng; Ma, Xiang; Dragnea, Bogdan; Kao, C. Cheng. Journal of Virology (2014), 88 (11), 6483-6491.

70. Hepatitis Virus Capsid Polymorph Stability Depends on Encapsulated Cargo Size. He, Li; Poterfield, Zachary; van der Schoot, Paul; Zlotnick, Adam; Dragnea, Bogdan. ACS Nano (2013), 7 (10), 8447-8454.
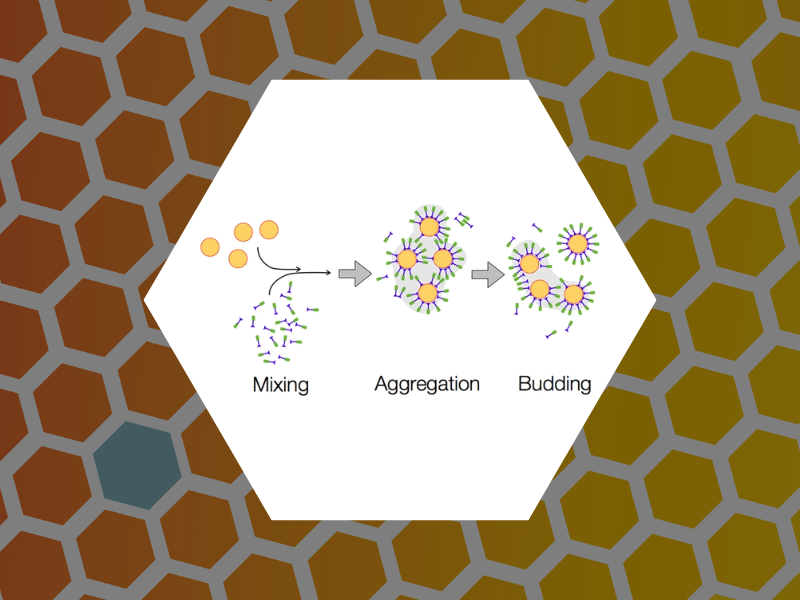
69. Budding Pathway in the Templated Assembly of Viruslike Particles. Malyutin, Andrey; Dragnea, Bogdan. Journal of Physical Chemistry B (2013), 117 (37), 10730-10736.

68. Fusion of mApple and Venus fluorescent proteins to the Sindbis virus E2 protein leads to different cell-binding properties. Tsvetkova, Irina; Cheng, Fan; Ma, Xiang; Moore, Alan; Howard, Benny; Mukhopadhyay, Suchetana; Dragnea, Bogdan. Virus Research (2013), 177 (2), 138-146.
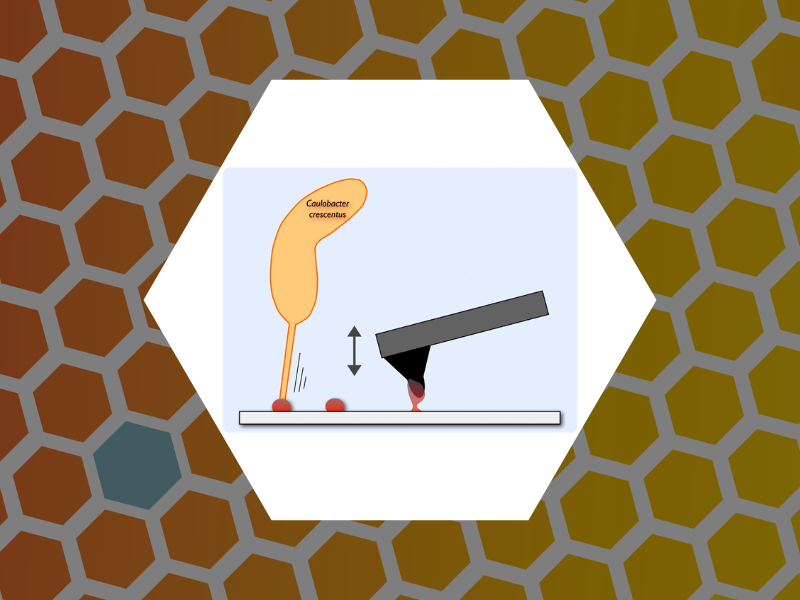
67. Physiochemical Properties of Caulobacter crescentus Holdfast: A Localized Bacterial Adhesive. Berne, Cecile; Ma, Xiang; Licata, Nicholas; Neves, Bernardo Ruegger Almeida; Setayeshgar, Sima; Brun, Yves; Dragnea, Bogdan. Journal of Physical Chemistry B (2013), 117 (36), 10492-10503.

66. The Packaging of Different Cargo into Enveloped Viral Nanoparticles. Cheng, Fan; Tsvetkova, Irina; Khuong, Y-Lan; Moore, Alan; Arnold, Randy; Goicochea, Nancy; Dragnea, Bogdan; Mukhopadhyay, Suchetana. Molecular Pharmaceutics (2013), 10(1), 51-58.
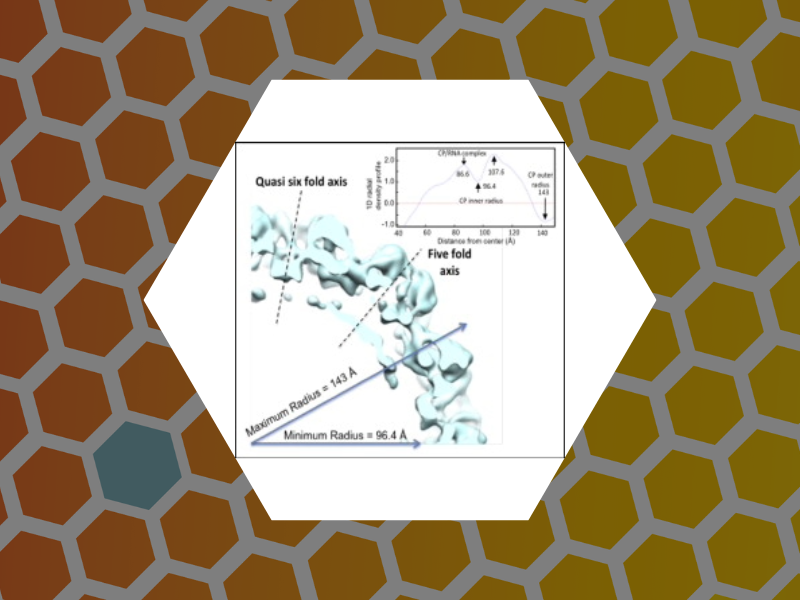
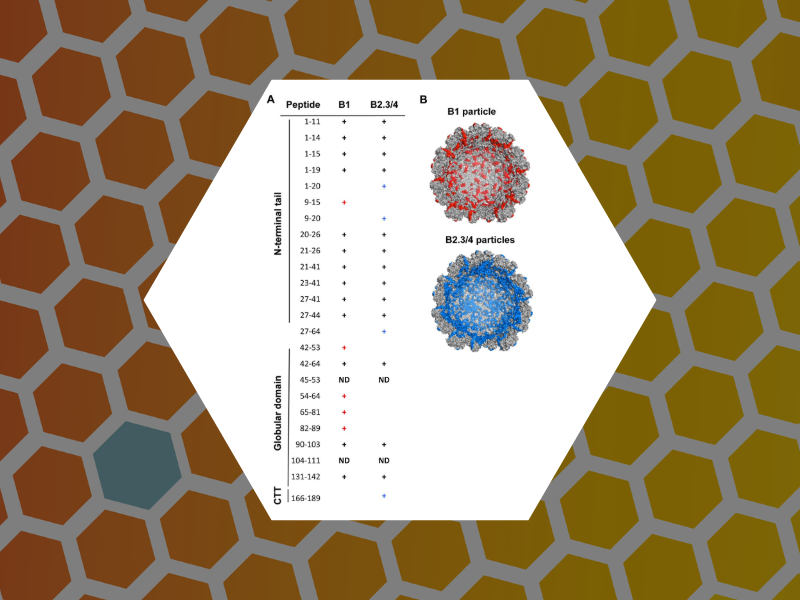
65. An Examination of the Electrostatic Interactions Between the N-Terminal Tail of the Brome Mosaic Virus Coat Protein and Encapsidated RNAs. Ni, Peng; Wang, Zhao; Ma, Xiang; Das Nayaran, Chandra; Sokol, Paul; Chiu, Wah; Dragnea, Bogdan; Hagan, Michael; Kao, Cheng. Journal of Molecular Biology (2012), 419(5), 284-300.
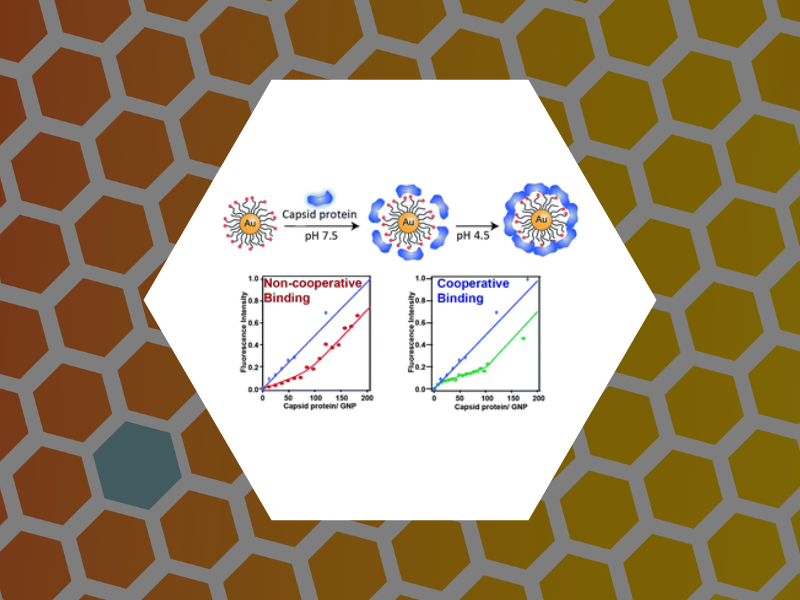
64. Pathway Switching in Templated Virus-Like Particle Assembly. Tsvetkova, Irina; Chen, Chao; Rana, Subinoy; Kao, Cheng; Rotello, Vincent; Dragnea, Bogdan. Soft Matter (2012), 8(17), 4570-4576.
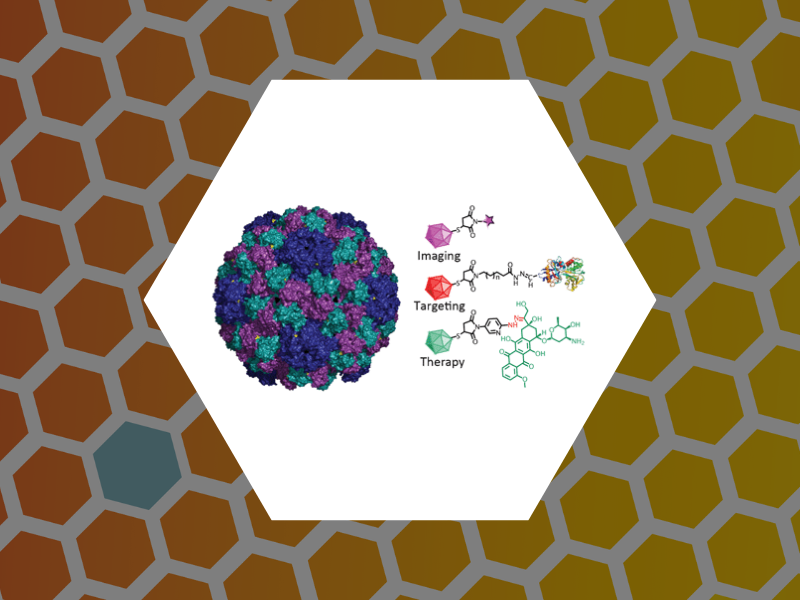
63. Engineering of Brome Mosaic Virus for Biomedical Applications. Yildiz, Ibrahim; Tsvetkova, Irina; Wen, Amy; Shukla, Sourabh; Masarapu, Hema; Dragnea, Bogdan; Steinmetz, Nicole. RSC Advances (2012), 2(9), 3670-3677.
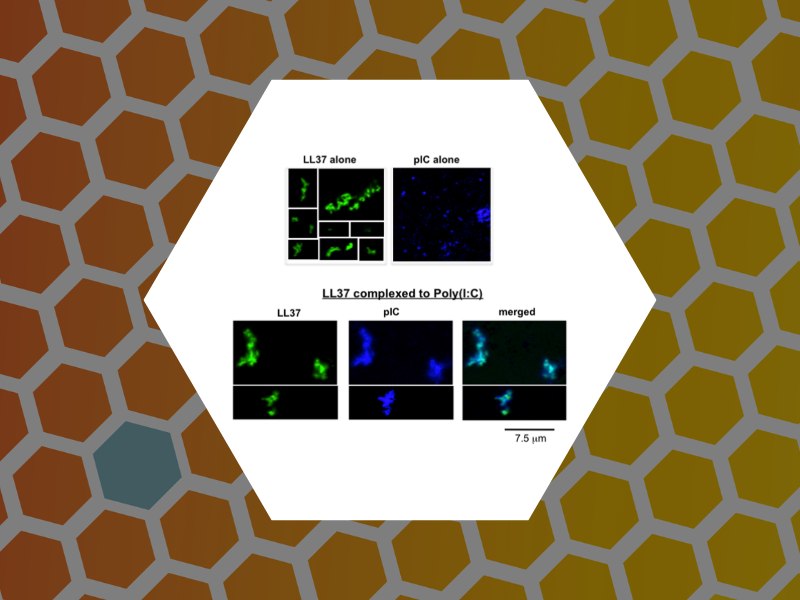
62. LL37 and Cationic Peptides Enhance TLR3 Signaling by Viral Double-stranded RNAs. Lai, Yvonne; Adhikarakunnathu, Sreedevi; Bhardwaj, Kanchan; Ranjith-Kumar, C.T.; Wen, Yahong; Jordan, Jarrat; Wu, Linda; Dragnea, Bogdan; San Mateo, Lani; Kao, Cheng. PLoS ONE (2011), 6(10), 1-14.
61. Conformationally Dynamic pi-Conjugation: Probing Structure-Property Relationships of Fluorescent Tris(N-salicylideneaniline)s. Vieweger, Mario; Jiang, Xuan; Young-Kwan, Lim; Jo, Junyong; Lee, Downgwhan; Dragnea, Bogdan. Journal of Physical Chemistry A (2011), 115(46), 13298-308.
60. Photothermal Imaging and Measurement of Protein Shell Stoichiometry of Single HIV-1 Gag Virus-like Nanoparticles. Vieweger, Mario; Goicochea, Nancy; Koh, Eun Sohl; Dragnea, Bogdan. ACS Nano (2011), 5(9), 7324-7333.
59. Structure and Stoichiometry of Template-Directed Recombinant HIV-1 Gag Particles. Goicochea, Nancy L.; Datta, Siddhartha A. K.; Ayaluru, Murali; Kao, Cheng; Rein, Alan; Dragnea, Bogdan. Journal of Molecular Biology (2011), 410, 667-680.
58. The coat protein leads the way: an update on basic and applied studies with the brome mosaic virus coat protein. Kao, C. Cheng; Ni, Peng; Hema, Masarapu; Huang, Xinlei; Dragnea, Bogdan. Molecular Plant Pathology (2011), 12(4),403-412.
57. Magnetic Virus-like Nanoparticles in N. benthamiana Plants: A New Paradigm for Environmental and Agronomic Biotechnological Research. Huang, Xinlei; Stein, Barry D.; Cheng, Hu; Malyutin, Andrey; Tsvetkova, Irina B.; Baxter, David V.; Remmes, Nicholas B.; Verchot, Jeanmarie; Kao, Cheng; Bronstein, Lyudmila M.; Dragnea, Bogdan. ACS Nano (2011), 5(5), 4037-4045. (Cover)
56. Slow Hot-Carrier Relaxation in Colloidal Graphene Quantum Dots. Mueller, Mallory L.; Yan, Xin; Dragnea, Bogdan; Li, Liang-shi. Nano Letters (2011), 11(1), 56-60.
55. Hydrophilization of Magnetic Nanoparticles with Modified Alternating Copolymers. Part 2: Bahavior in Solution. Shtykova, Eleonora V.; Malyutin, Andrey; Dyke, Jason C.; Stein, Barry; Konarev, Peter V.; Dragnea, Bogdan; Svergun, Dmitri I.; Bronstein, Lyudmila M. Journal of Physical Chemistry C (2010), 114(50), 21908-21913.
54. Hydrophilization of Magnetic Nanoparticles with Modified Alternating Copolymers. Part 1: The Influence of the Grafting. Bronstein, Lyudmila M.; Shtykova, Eleonora V.; Malyutin, Andrey; Dyke, Jason C.; Gunn, Emily; Gao, Xinfeng; Stein, Barry; Konarev, Peter V.; Dragnea, Bogdan; Svergun, Dmitri I. Journal of Physical Chemistry C (2010), 114(50), 21900-21907.
53. Effects of amino-acid substitutions in the Brome mosaic virus capsid protein on RNA encapsidation. Hema, Masarapu; Murali, Ayaluru; Ni, Peng; Vaughan, Robert C.; Fujisaki, Koki; Tsvetkova, Irina; Dragnea, Bogdan; Kao, C. Cheng. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 23(11), 1433-1447 (2010).
52. Role of Surface Charge Density in Nanoparticle-Templated Assembly of Bromovirus Protein Cages. Daniel, Marie-Christine; Tsvetkova, Irina B.; Quinkert, Zachary T.; Murali, Ayaluru; De, Mrinmoy; Rotello, Vincent M.; Kao, C. Cheng; Dragnea, Bogdan. ACS Nano, 4(7), 3853-3860 (2010).
51. Bio-enabled synthesis of metamaterials. DuFort Christopher C; Dragnea, Bogdan. Annual Review of Physical Chemistry, 61, 323-344 (2010).
50. Bionanodesign: Following Nature’s Touch. Dragnea, Bogdan. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 132(4), 1443-1444 (2010).
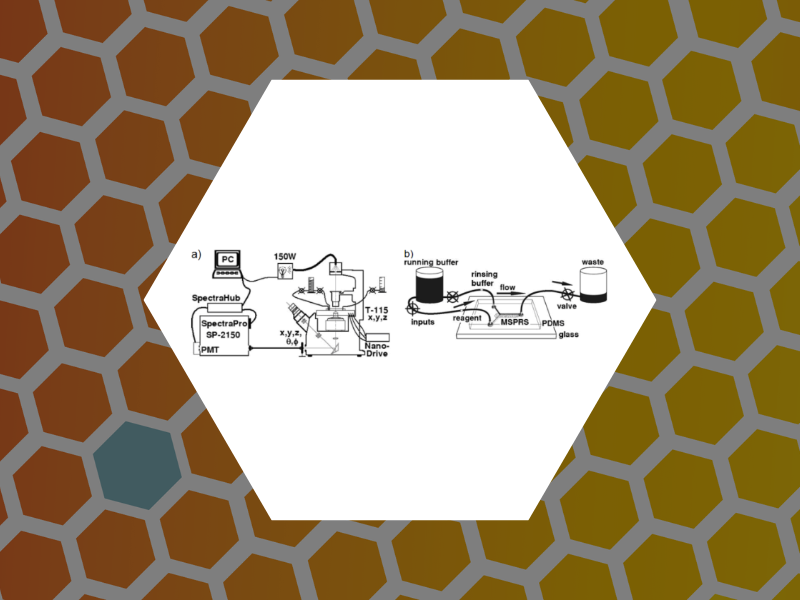
49. Microfluidic Devices Integrating Microcavity Surface-Plasmon-Resonance Sensors: Glucose Oxidase Binding-Activity Detection. Amarie, Dragos; Alileche, Abdelkrim; Dragnea, Bogdan; Glazier, James A. Analytical Chemistry, 82(1), 343-352 (2010).
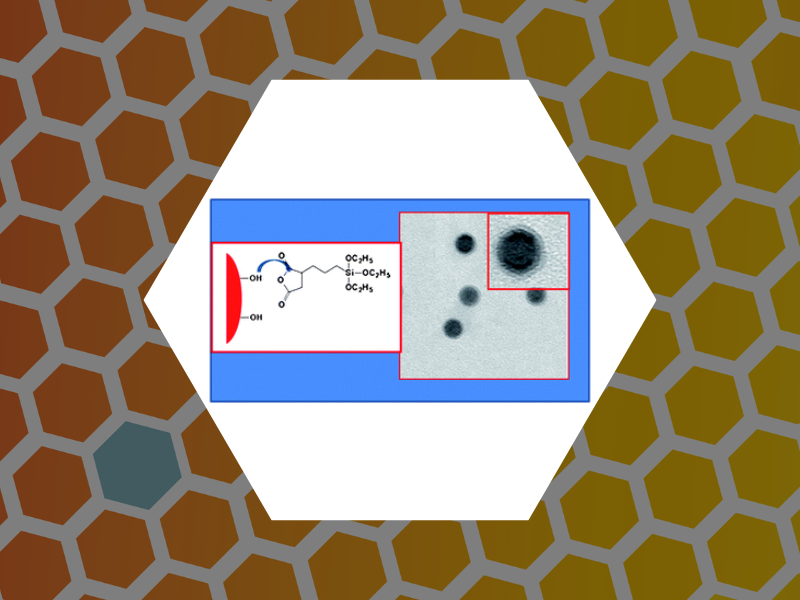
48. Magnetic nanoparticles with functional silanes: Evolution of well-defined shells from anhydride containing silanes, Huang, Xinlei; Schmucker, Abrin; Dyke, Jason; Hall, Sara M.; Retrum, John; Stein, Barry; Remmes, Nicholas; Baxter, David V.; Dragnea, Bogdan; Bronstein, Lyudmila M. Journal of Materials Chemsitry, 19(24), 4231-4239 (2009).
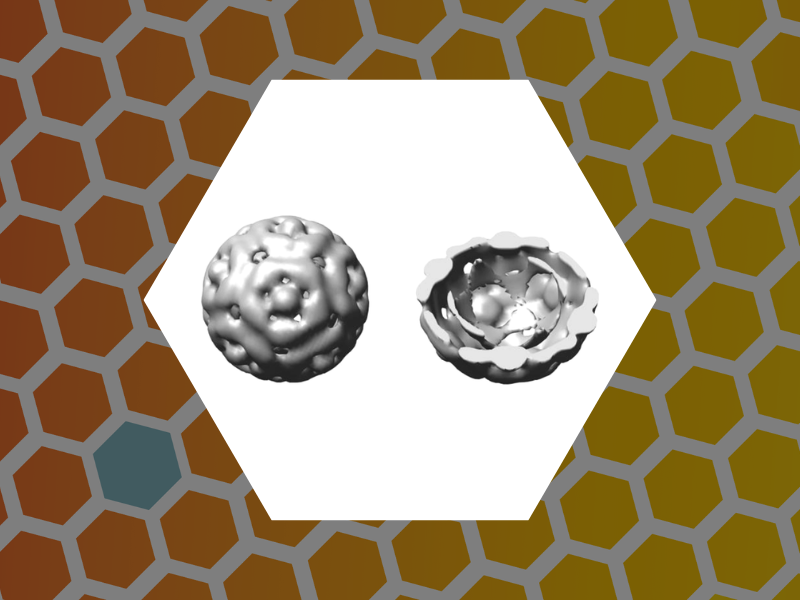
47. Synergistic Effects of Mutations and Nanoparticle Templating in the Self-Assembly of Cowpea Chlorotic Mottle Virus Capsids, Aniagyei, Stella E.; Kennedy, Chelsea J.; Stein, Barry; Willits, Deborah A.; Douglas, Trevor; Young, Mark J.; De, Mrinmoy; Rotello, Vincent M.; Srisathiyanarayanan, D.; Kao, C. Cheng; Dragnea, Bogdan. Nano Letters, 9(1), 393-398 (2009).
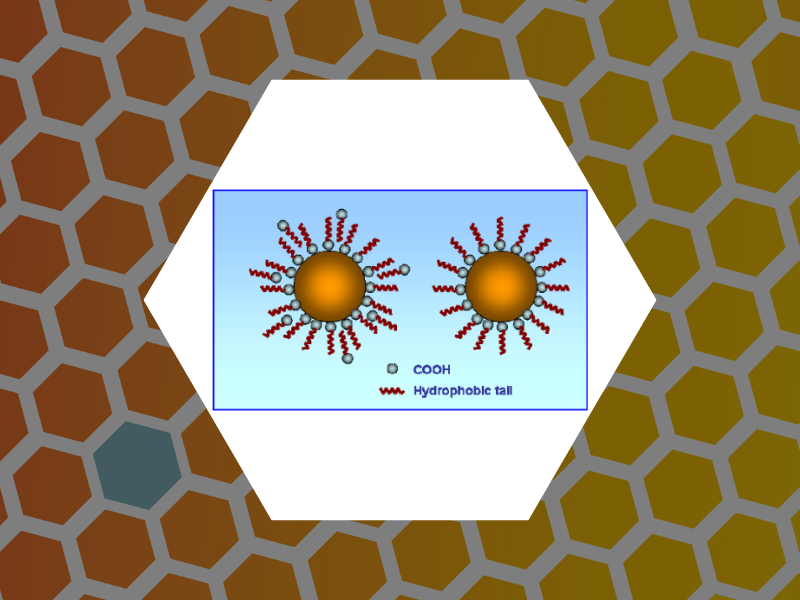
46. Hydrophilic Monodisperse Magnetic Nanoparticles Protected by an Amphiphilic Alternating Copolymer, Shtykova, Eleonora V.; Huang, Xinlei; Gao, Xinfeng; Dyke, Jason C.; Schmucker, Abrin L.; Dragnea, Bogdan; Remmes, Nicholas; Baxter, David V.; Stein, Barry; Konarev, Peter V.; Svergun, Dmitri I.; Bronstein, Lyudmila M. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 112(43), 16809-16816 (2008).

45. Self-Assembly of Brome Mosaic Virus Capsids: Insights from Shorter Time-Scale Experiments, Chen, Chao; Kao, C. Cheng; Dragnea, Bogdan. J. Phys. Chem. A, 112(39),9405-9412 (2008).
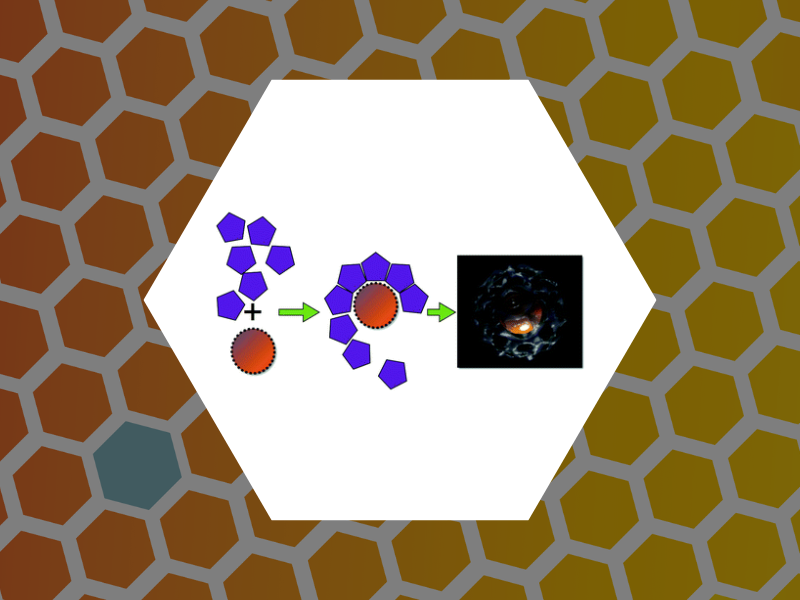
44. Self-assembly approaches to nanomaterial encapsulation in viral protein cages, Aniagyei, Stella E.; DuFort, Christopher; Kao, C. Cheng; Dragnea, Bogdan. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 18(32), 3763-3774 (2008).
43. Well-defined hybrid magnetic nanoparticles by self-assembly, Bronstein, Lyudmila M.; Huang, Xinlei; Dyke, Jason; Schmucker, Abrin Lee; Dufort, Chris; Shtykova, Eleonora V.; Svergun, Dmitri I.; Dragnea, Bogdan; PMSE Preprints, 98, 115-116 (2008).
42. Unnatural life, Dragnea, Bogdan. Nature Materials, 7(2), 102-104 (2008).

41. Structure and Properties of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Encapsulated by Phospholipids with Poly(ethylene glycol) Tails, Shtykova, Eleonora V.; Huang, Xinlei; Remmes, Nicholas; Baxter, David; Stein, Barry; Dragnea, Bogdan; Svergun, Dmitri I.; Bronstein, Lyudmila M. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 111(49), 18078-18086 (2007).

40. Core-like Particles of an Enveloped Animal Virus Can Self-Assemble Efficiently on Artificial Templates, Goicochea, Nancy L.; De, Mrinmoy; Rotello, Vincent M.; Mukhopadhyay, Suchetana; Dragnea, Bogdan. Nano Letters, 7(8), 2281-2290 (2007).

39. Reactivity-Based Fluoride Detection: Evolving Design Principles for Spring-Loaded Turn-On Fluorescent Probes, Jiang, Xuan; Vieweger, Mario C.; Bollinger, John C.; Dragnea, Bogdan; Lee, Dongwhan. Organic Letters, 9(18), 3579-3582 (2007).

38. Self-Assembled Virus-like Particles with Magnetic Cores, Huang, Xinlei; Bronstein, Lyudmila M.; Retrum, John; Dufort, Chris; Tsvetkova, Irina; Aniagyei, Stella; Stein, Barry; Stucky, Galen; McKenna, Brandon; Remmes, Nicholas; Baxter, David; Kao, C. Cheng; Dragnea, Bogdan. Nano Letters, 7(8), 2407-2416 (2007).

37. Influence of Iron Oleate Complex Structure on Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Formation, Bronstein, Lyudmila M.; Huang, Xinlei; Retrum, John; Schmucker, Abrin; Pink, Maren; Stein, Barry D.; Dragnea, Bogdan. Chemistry of Materials, 19(15), 3624-3632 (2007).

36. Optical Field Enhancement at Cusps between Adjacent Nanoapertures, Onuta, Tiberiu-Dan; Waegele, Matthias; DuFort, Christopher C.; Schaich, William L.; Dragnea, Bogdan. Nano Letters, 7(3), 557-564 (2007).
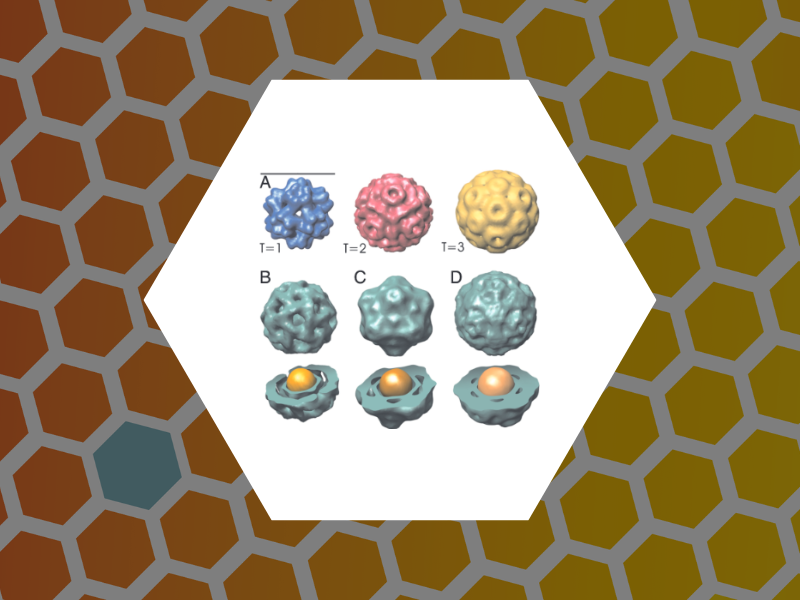
35. Core-controlled polymorphism in virus-like particles, Sun, Jingchuan; DuFort, Chris; Daniel, Marie-Christine; Murali, Ayaluru; Chen, Chao; Gopinath, Kodetham; Stein, Barry; De, Mrinmoy; Rotello, Vincent M.; Holzenburg, Andreas; Kao, C. Cheng; Dragnea, Bogdan. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(4), 1354-1359 (2007).
34. Functionalized magnetic nanoparticles: Morphology-property relationship, Bronstein, Lyudmila M.; Huang, Xinlei; Retrum, John; Stein, Barry; Remmes, Nicholas B.; Baxter, David V.; Dixit, Suraj; Dragnea, Bogdan; Polymer Preprints (American Chemical Society, Division of Polymer Chemistry), 47(2), 849-850 (2006).
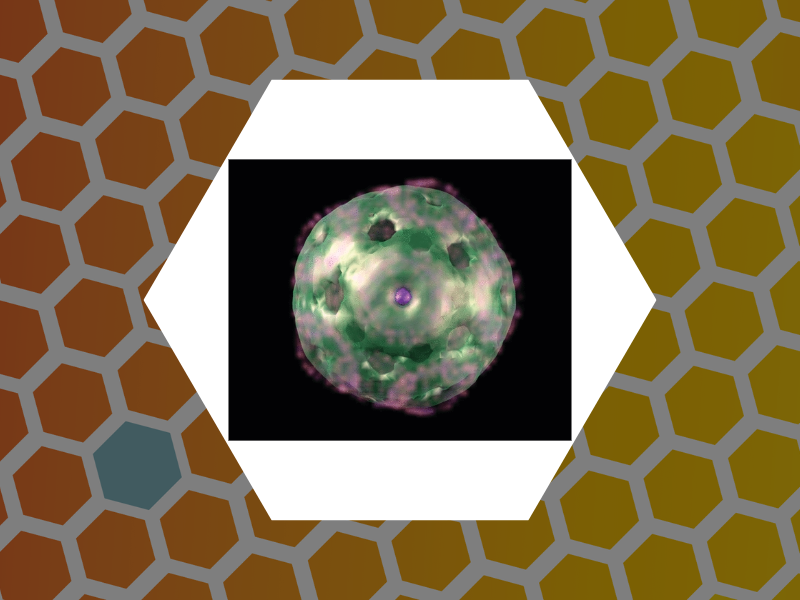
33. Quantum Dot Encapsulation in Viral Capsids, Dixit, Suraj K.; Goicochea, Nancy L.; Daniel, Marie-Christine; Murali, Ayaluru; Bronstein, Lyudmila; De, Mrinmoy; Stein, Barry; Rotello, Vincent M.; Kao, C. Cheng; Dragnea, Bogdan. Nano Letters, 6(9), 1993-1999 (2006).
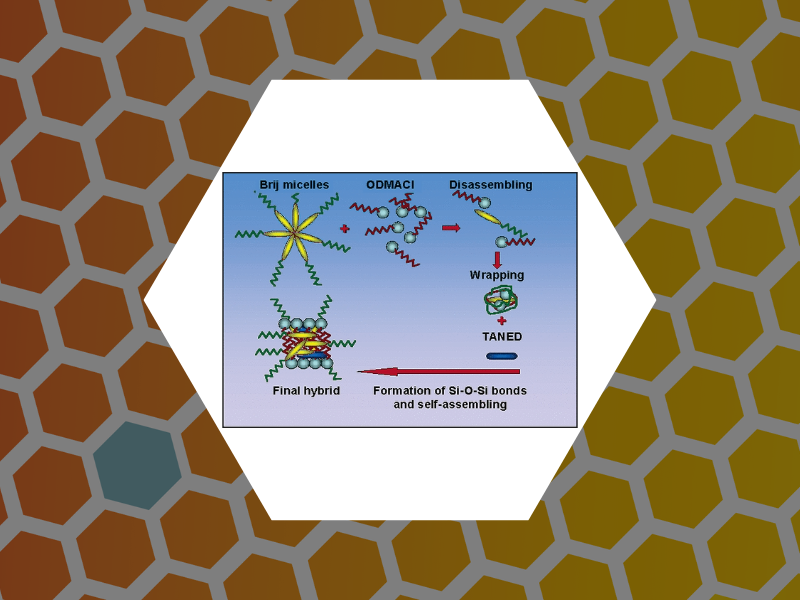
32. Hybrid Polymer Particles with a Protective Shell: Synthesis, Structure, and Templating, Bronstein, Lyudmila M.; Dixit, Suraj; Tomaszewski, John; Stein, Barry; Svergun, Dmitri I.; Konarev, Peter V.; Shtykova, Eleonora; Werner-Zwanziger, Ulrike; Dragnea, Bogdan. Chemistry of Materials, 18(9), 2418-2430 (2006).
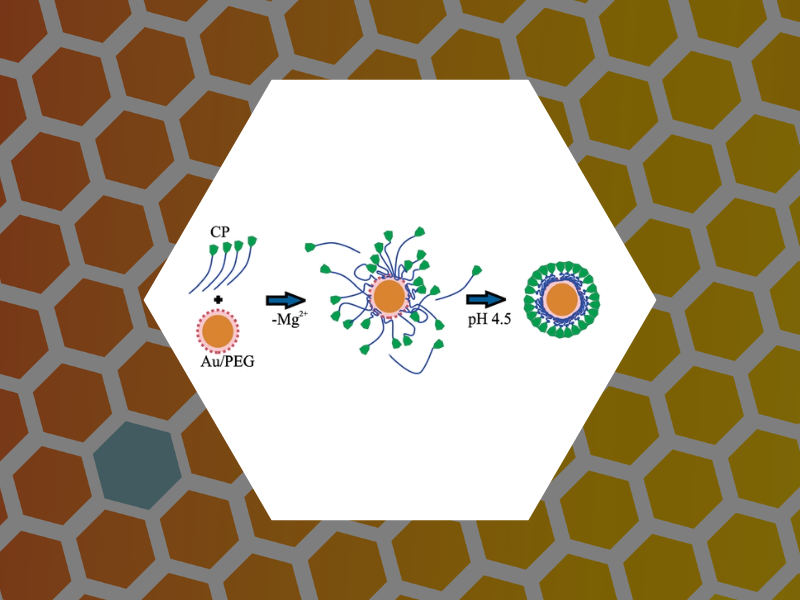
31. Nanoparticle-Templated Assembly of Viral Protein Cages, Chen, Chao; Daniel, Marie-Christine; Quinkert, Zachary T.; De, Mrinmoy; Stein, Barry; Bowman, Valorie D.; Chipman, Paul R.; Rotello, Vincent M.; Kao, C. Cheng; Dragnea, Bogdan. Nano Letters, 6(4), 611-615 (2006).

30. Packaging of gold particles in viral capsids, Chen, Chao; Kwak, Eun-Soo; Stein, Barry; Kao, C. Cheng; Dragnea, Bogdan. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 5(12), 2029-2033 (2005).
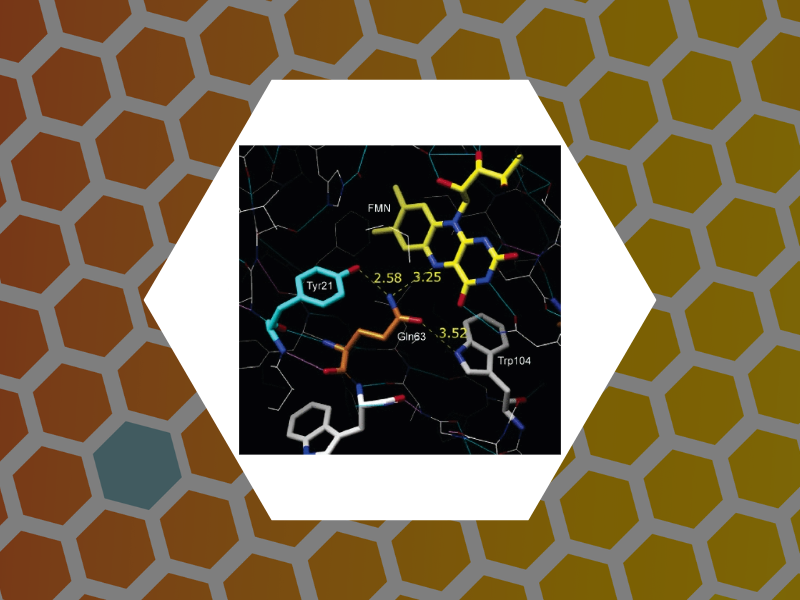
29. Time-Resolved Spectroscopic Studies of the AppA Blue-Light Receptor BLUF Domain from Rhodobacter sphaeroides, Dragnea, Vladimira; Waegele, Matthias; Balascuta, Septimiu; Bauer, Carl; Dragnea, Bogdan. Biochemistry, 44(49), 15978-15985 (2005).

28. Interaction between Brome mosaic virus proteins and RNAs: Effects on RNA replication, protein expression, and RNA stability, Gopinath, K.; Dragnea, B.; Kao, C. Journal of Virology, 79(22), 14222-14234 (2005).

27. Submicrometer Cavity Surface Plasmon Sensors, Amarie, Dragos; Onuta, Tiberiu-Dan; Potyrailo, Radislav A.; Dragnea, Bogdan. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 109(32), 15515-15519 (2005).
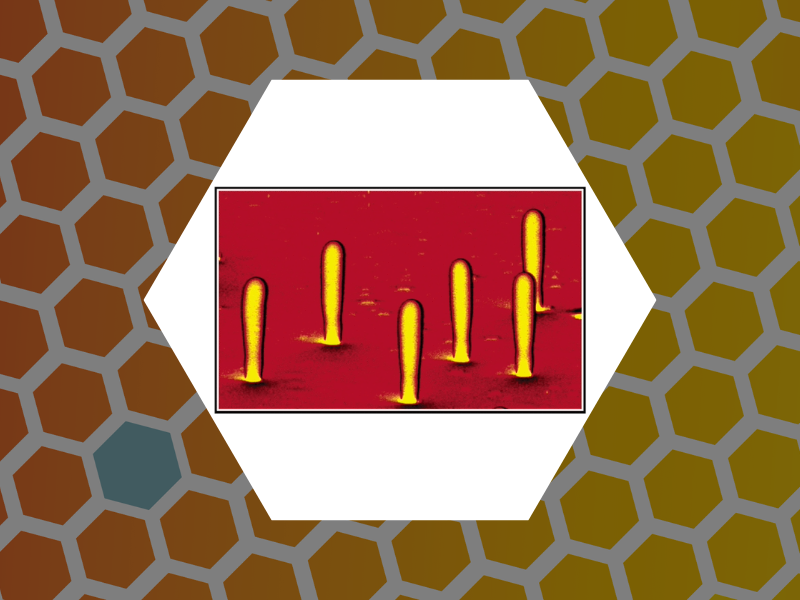
26. Three-Dimensional Mapping of the Light Intensity Transmitted through Nanoapertures, Amarie, Dragos; Rawlinson, Nathan D.; Schaich, William L.; Dragnea, Bogdan; Jacobson, Stephen C. Nano Letters, 5(7), 1227-1230 (2005).

25. Fluctuation correlation spectroscopy of near-field trapped nanoparticles, Onuta, Tiberiu-Dan; Schaich, William L.; Dragnea, Bogdan G; Proceedings of SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering, 5736 (Nanomanipulation with Light), 25-29 (2005), DOI:10.1117/12.591679.

24. Optical Trapping with Integrated Near-Field Apertures, Kwak, Eun-Soo; Onuta, Tiberiu-Dan; Amarie, Dragos; Potyrailo, Radislav; Stein, Barry; Jacobson, Stephen C.; Schaich, W. L.; Dragnea, Bogdan. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 108(36), 13607-13612 (2004).
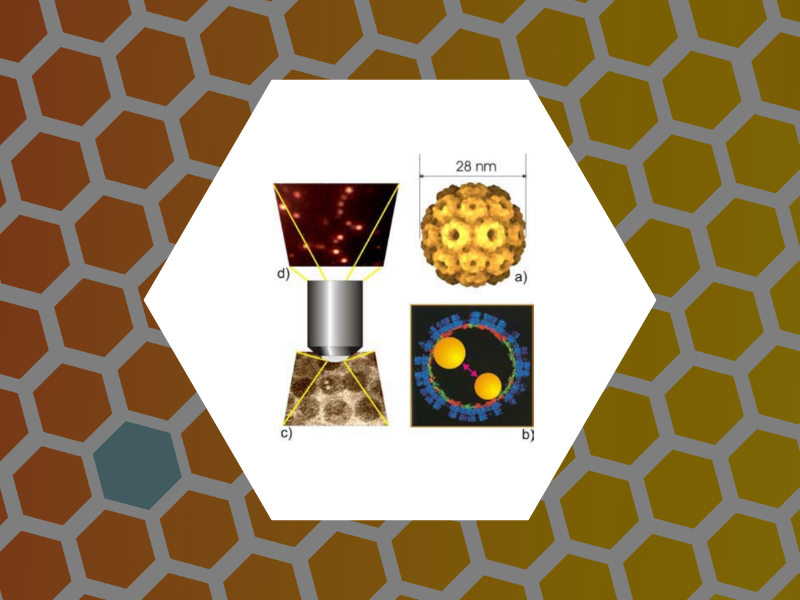
23. Viruses as optical probes, Kwak, E.-S.; Chen, C.; Kao, C. Cheng; Schaich, W. L.; Dragnea, B. Editor(s): Laudon, Matthew; Romanowicz, Bart; NSTI Nanotech 2004, NSTI Nanotechnology Conference and Trade Show, Boston, MA, 1, 11-14 (2004).

22. Field-Induced Interfacial Properties of Gold Nanoparticles in AC Microelectrophoretic Experiments, Kloepper, Kathryn D.; Onuta, Tiberiu-Dan; Amarie, Dragos; Dragnea, Bogdan. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 108(8), 2547-2553 (2004).

21. Chemical Imaging NSOM, Dragnea, B; in the Dekker Encyclopedia of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 1st edition, Marcel Dekker, NY, (2004).

20. Gold nanoparticles as spectroscopic enhancers for in vitro studies on single viruses, Dragnea, Bogdan; Chen, Chao; Kwak, Eun-Soo; Stein, Barry; Kao, C. Cheng. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 125(21), 6374-6375 (2003).

19. Water Vapor Uptake in Photolithographic Polymers Observed by Infrared Near-Field Scanning Optical Microscopy in a Controlled Environment, McDonough, Laurie A.; Dragnea, Bogdan; Preusser, Jan; Leone, Stephen R.; Hinsberg, William D. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 107(21), 4951-4954 (2003).

18. Near-Field Surface Plasmon Excitation on Structured Gold Films, Dragnea, Bogdan; Szarko, Jodi M.; Kowarik, Stefan; Weimann, Thomas; Feldmann, Jochen; Leone, Stephen R. Nano Letters, 3(1), 3-7 (2003).(Cover)

16. Growth of a SiC layer on Si(100) from adsorbed propene by laser melting, Dragnea, Bogdan; Boulmer, Jacques; Debarre, Dominique; Bourguignon, Bernard. Applied Physics A: Materials Science & Processing, 73(5), 609-613 (2001).

17. Influence of adsorbates on UV-pulsed laser melting of Si in ultra-high vacuum, Dragnea, B.; Boulmer, J.; Debarre, D.; Bourguignon, B. Applied Physics A: Materials Science & Processing, 73(5), 609-613 (2001).

15. Chemical mapping of patterned polymer photoresists by near-field infrared microscopy. Dragnea, B.; Preusser, J.; Szarko, J. M.; McDonough, L. A.; Leone, S. R.; Hinsberg, W. D; Applied Surface Science,175-176, 783-789 (2001).

14. Advances in submicron infrared vibrational band chemical imaging, Dragnea, Bogdan; Leone, Stephen R. International Reviews in Physical Chemistry, 20(1), 59-92 (2001).
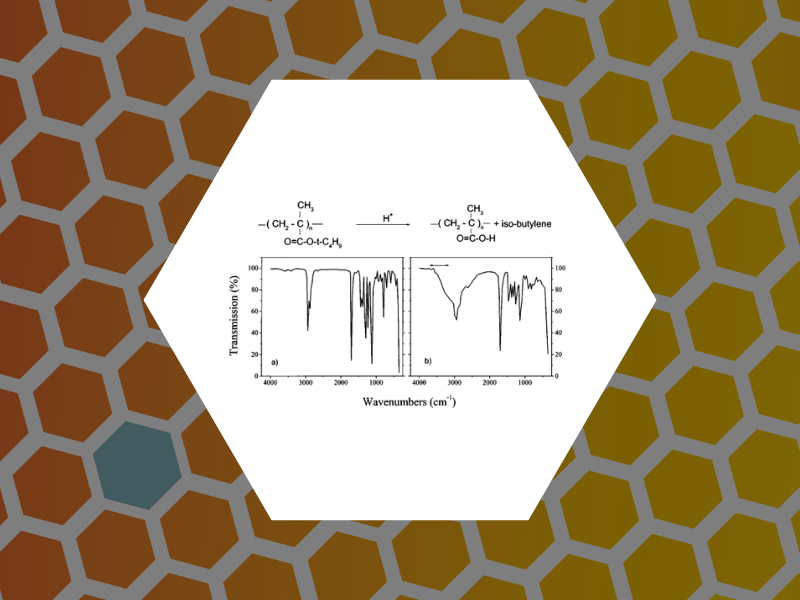
13. Pattern characterization of deep-ultraviolet photoresists by near-field infrared microscopy, Dragnea, Bogdan; Preusser, Jan; Szarko, Jodi M.; Leone, Stephen R.; Hinsberg, William D. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology, B: 13. Microelectronics and Nanometer Structures, 19(1), 142-152 (2001).
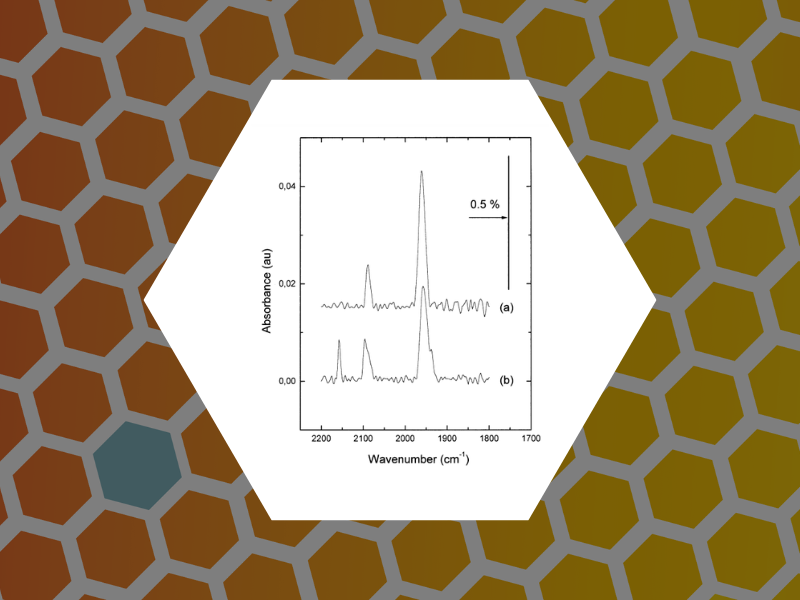
12. Site selective probe of the desorption of CO from Pd(111) by sum frequency generation and Fourier transform IR: a comparison of thermal and laser desorption, Carrez, Serge; Dragnea, Bogdan; Zheng, Wan Quan; Dubost, Henri; Bourguignon, Bernard. Surface Science, 440(1-2), 151-162 (1999).

11. Transmission near-field scanning microscope for infrared chemical imaging, Dragnea, Bogdan; Preusser, Jan; Schade, Wolfgang; Leone, Stephen R.; Hinsberg, William D. Journal of Applied Physics, 86(5), 2795-2799 (1999).

10. Photoinduced effects in UV laser melting of Si in UHV, Dragnea, Bogdan. Physical Review Letters, 82(15), 3085-3088 (1999).

9. Vibrational spectroscopy of imperfect CO/Pd(111) surfaces obtained by adsorption between 150 and 230 K, Bourguignon, Bernard; Carrez, Serge; Dragnea, Bogdan; Dubost, Henri. Surface Science, 418(1), 171-180 (1998).

8. Laser induced structural or compositional modifications of Si or IV-IV surface: planarization, pulsed laser induced epitaxy, carbon incorporation, chemical etching, Boulmer, J.; Dragnea, B.; Guedj, C.; Debarre, D.; Bosseboeuf, A.; Finkman, E.; Bourguignon, B. Proceedings of SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering, 3404(Laser Surface Processing), 149-158 (1998), DOI: 10.1117/12.308609.
7. Laser-induced annealing and etching of silicon: experiments and mathematical simulations, Bourguignon, B.; Dragnea, B.; Boulmer, J.; Budin, J. -P.; Debarre, D; Annales de Physique (Paris), 22(Colloq. 1), C1/229-C1/236 (1997).
6. Desorption and diffusion at pulsed-laser-melted surfaces: The case of chlorine on silicon, Dragnea, Bogdan; Boulmer, Jacques; Budin, Jean-Pierre; Debarre, Dominique; Bourguignon, Bernard. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter, 55(20), 13904-13915 (1997).

5. Laser modifications of Si(100):Cl surfaces induced by surface melting: etching and cleaning, Bourguignon, B.; Stoica, M.; Dragnea, B.; Carrez, S.; Boulmer, J.; Budin, J.-P.; Debarre, D.; Aliouchouche, A. Surface Science, 338(1-3), 94-110 (1995).

4. IR and UV laser-assisted deposition from titanium tetrachloride: a comparative study, Alexandrescu, R.; Cireasa, R.; Dragnea, B.; Morjan, I.; Voicu, I.; Andrei, A.; Visiliu, F.; Popescu, C. Advanced Materials for Optics and Electronics, 5(1), 19-30 (1995).

3. Laser-induced photodeposition from ZnS colloid solutions, Peled, A.; Dragnea, B.; Alexandrescu, Rodica; Andrei, A. Applied Surface Science, 86(1-4), 538-42 (1995).

2. Field distribution effects in laser driven diffusion through metal capillaries. Dragnea, Bogdan. Infrared Physics & Technology, 35(6), 765-73 (1994).